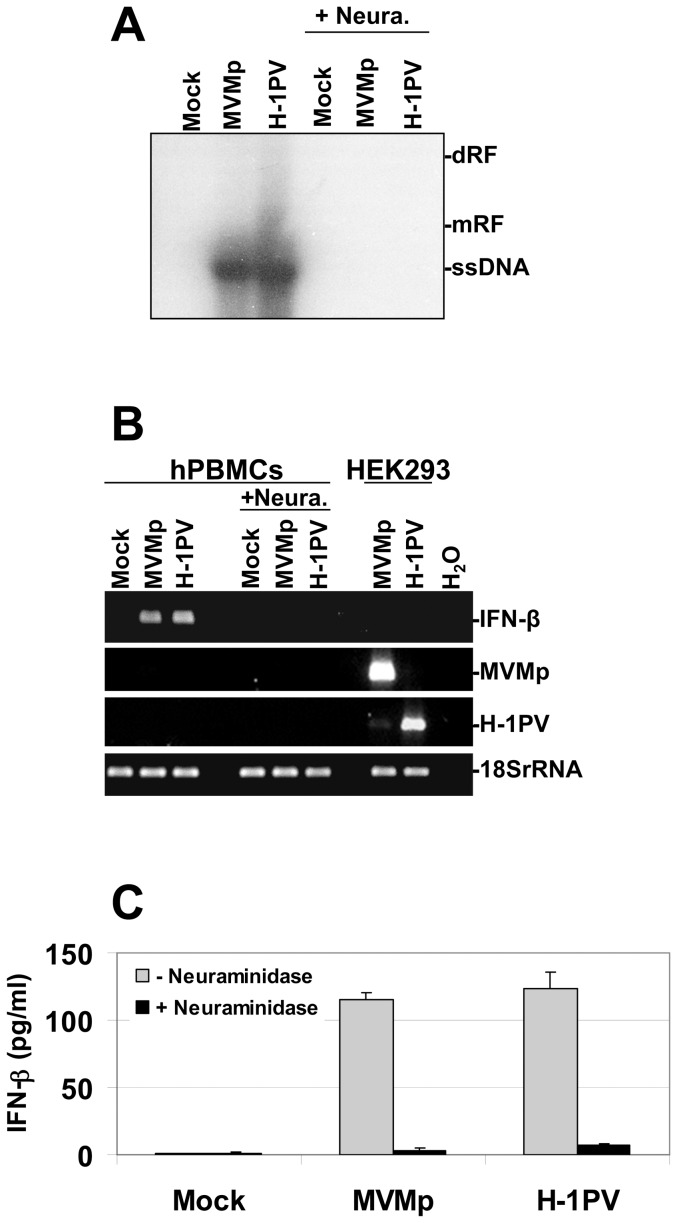
Figure 8. Sensitivity to neuraminidase pre-treatment of the antiviral response triggered by parvoviruses in hPBMCs.
(A to C) hPBMCs collected from the blood of healthy donors were distributed into 6-well plates at 1×107 cells/5 ml culture medium/well. They were then treated or not with neuraminidase at 0.1 U/ml for 15 hrs and then mock-treated or infected with MVMp or H-1PV at 20 PFUs/cell. (B) In parallel to the treatment of PBMCs, HEK293 cells cultivated in 10-cm dishes at a density of 1.5 106 cells/dish were also mock-treated or infected with MVMp or H-1PV at 2 PFUs/cell. Cells (A, B) as well as supernatants (C) were isolated 24 hrs p.i. in order to perform Southern blot (A), RT-PCR (B), and ELISA (C) experiments. (A) DNA was extracted from hPBMCs and Southern blotting performed as described in Figure 2. (dRF, dimmer replicative form; mRF, monomeric replicative form; ssDNA, single-stranded genome). The blot shown is representative of 3 experiments which all gave similar results. (B) Total RNA extraction and consecutive synthesis of cDNA from hPBMC and HEK293 cultures were performed as described in Figure 1. Expression of the indicated transcripts was assessed using specific pairs of primers. Transcripts encoding the human 18S ribosomal protein were used as internal loading controls. Data shown are representative of 3 experiments that gave similar results. (C) Collected supernatants were centrifuged in order to discard cellular debris and analyzed by Enzyme-linked Immuno-Sorbent Assay (ELISA) for their content in IFN-α and IFN-β cytokines. Results are expressed as means+standard deviations of three independent experiments. Each presented blot is representative of 3 experiments which gave similar results.