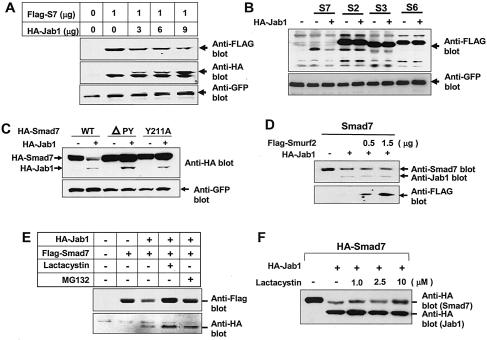
FIG. 5.
Jab1/CSN5 induces degradation of Smad7. (A) Ectopic expression of Jab1/CSN5 down regulates Smad7. HepG2 cells were transfected with increasing amounts of HA-Jab1/CSN5 expression vector or control plasmid together with Flag-Smad7 expression vector. A GFP expression construct was used as the control. After 24 h, cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against HA, Flag, and GFP. (B) Jab1/CSN5 specifically degrades Smad7 but not Smad2, Smad3, or Smd6. HepG2 cells were transfected with HA-Jab1 expression construct or control plasmid together with the vectors indicated at the top, and after 24 h, total cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-Flag antibody. (C) The PY motif in Smad7 is important for Jab1-/CSN5-mediated degradation of Smad7. 293T cells were transfected with HA-Jab1/CSN5 or control plasmid together with either wild-type (WT), ΔPY, or mutant Y211A versions of Smad7. Total cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting by using anti-HA antibody, and Smad7 and Jab1/CSN5 were identified on the basis of their molecular weights. A GFP expression construct was used as the loading control. (D) Effect of Smurf2 on the Jab1-mediated degradation of Smad7. A Smad7 expression construct was transfected into 293T cells with either HA-Jab1/CSN5 alone or together with increasing amounts of Flag-Smurf2 expression vector. Total cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against Smad7, Jab1, and Flag. (E and F) Degradation of Smad7 by Jab1/CSN5 is sensitive to 26S proteosome inhibitors. 293T cells transfected with Flag-Smad7 alone or together with HA-Jab1/CSN5 were incubated with lactacystin (10 μM) or MG132 (2 μM), and expression of Flag-Smad7 was analyzed by immunoblotting.