Figure 3.
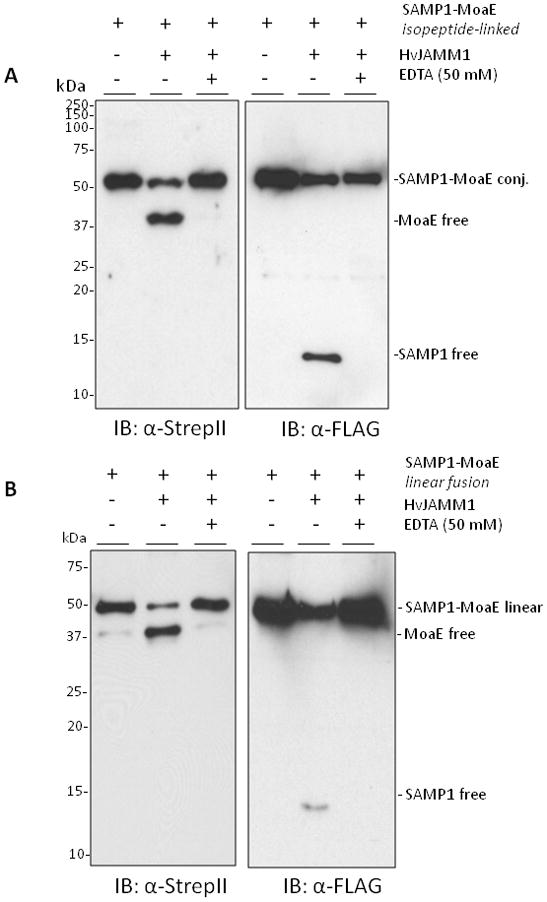
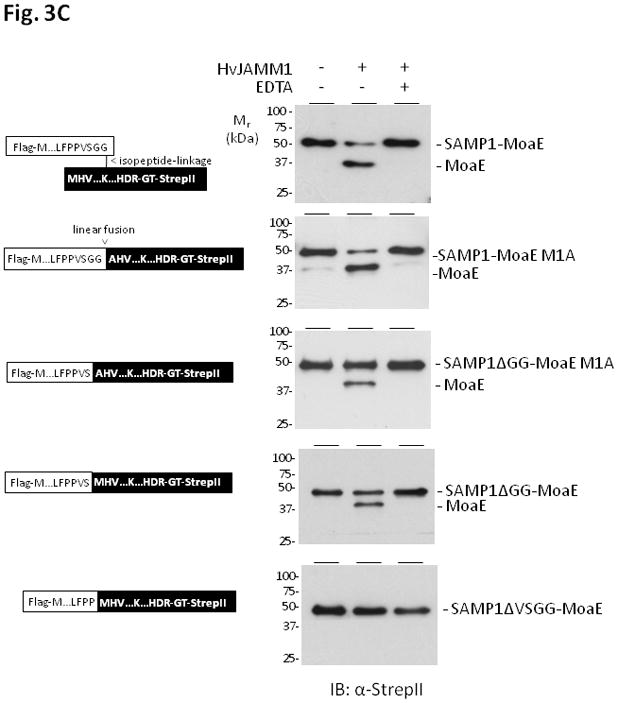
HvJAMM1releases SAMP1 from isopeptide (A) and linear (B and C) linkages to MoaE. Desampylation activity was monitored by α-Flag and α-StrepII immunoblot where the Flag-tag is incorporated at the N-terminus of SAMP1 and the StrepII tag is incorporated at the C-terminus of MoaE. Site-directed modifications were incorporated into the linear peptide bond linking SAMP1 to MoaE, and EDTA was included to inactivate HvJAMM1 as indicated. Protein bands specific for the free and conjugated forms of SAMP1 and MoaE migrated slower in SDS-PAGE gels than their theoretical molecular masses (i.e., 39 kDa for FLAG-SAMP1-MoaE-StrepII, 29 kDa for MoaE-StrepII, 12 for FLAG-SAMP1). This slow migration is similar to HvJAMM1 (this study), H. volcanii 20S proteasomes (Wilson et al., 1999) and other proteins such as eukaryotic Ub and Ub-like proteins (Van der Veen and Ploegh, 2012).
