Figure 5.
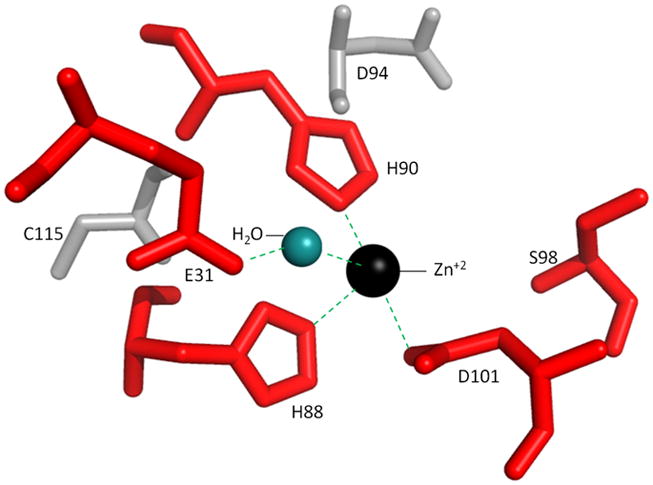
Active site region of HvJAMM1 modeled using AfJAMM as template. The catalytic zinc ion and water (not to scale) are included to assist in understanding the mechanism of HvJAMM1-mediated desampylation. E31, H88, H90, S98 and D101 (red) are conserved active site residues predicted to be required for HvJAMM1 activity.
