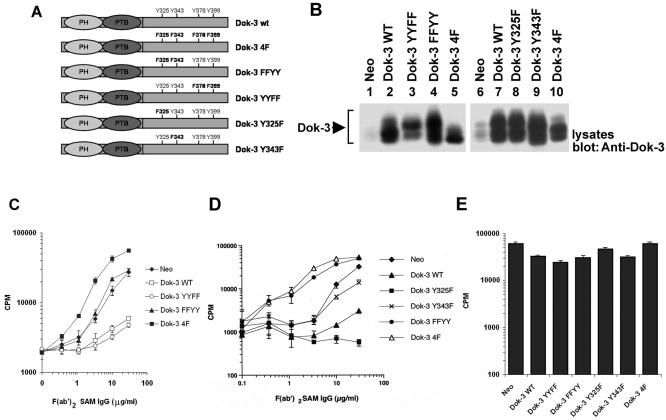
FIG. 1.
Tyrosines 325 and 343 are required for the inhibitory effect of Dok-3 in A20 B cells. (A) Primary structures of the Dok-3 mutants created for this study. The positions of the PH and PTB domains, as well as of the four carboxyl-terminal tyrosines, are highlighted. (B) Expression of the various Dok-3 polypeptides in A20 B cells. The expression of Dok-3 in pools of three independent transfectants for each of the Dok-3-encoding constructs was measured by immunoblotting of equivalent amounts of total cell proteins with anti-Dok-3. (C) Impact of Dok-3 YYFF and Dok-3 FFYY on BCR-induced IL-2 secretion. Pools of three transfectants were activated for 24 h with the indicated amounts of F(ab′)2 fragments of SAM IgG. IL-2 release was determined in a bioassay using the IL-2-dependent T-cell line HT-2. Assays were done in triplicate, and average values with standard deviations are shown. (D) Effect of Dok-3 Y325F and Dok-3 Y343F on BCR-triggered IL-2 production. The experiment was conducted as outlined for panel C, except that other transfectants were tested. (E) Influence of Dok-3 polypeptides on responsiveness to PMA plus ionomycin. Cells were stimulated for 24 h with PMA and ionomycin. IL-2 secretion was subsequently measured as described for panel C.