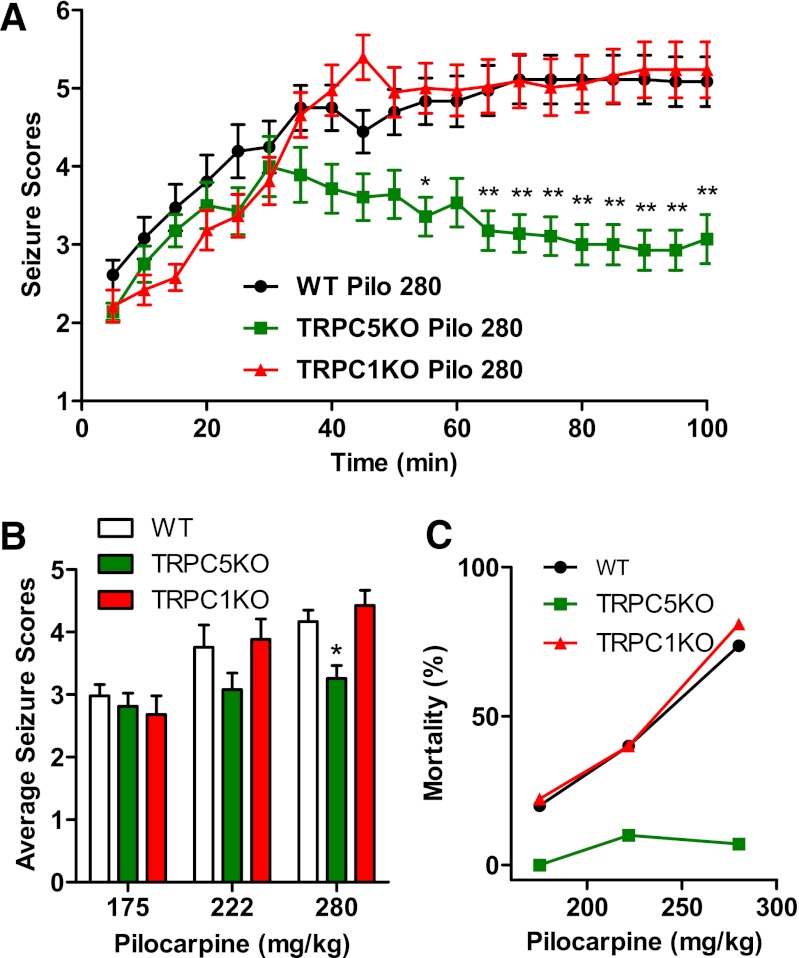
Fig. 2.
Pilocarpine-induced seizures were significantly reduced in TRPC5 KO mice. (A) The time course of pilocarpine-induced seizures in WT, TRPC5KO, and TRPC1KO mice after a single injection of pilocarpine (280 mg/kg, i.p.). Pooled data (mean ± S.E.M.) was plotted (n = 18, 14, and 19 for WT, TRPC5KO, and TRPC1 KO, respectively). See Phelan et al. (2012) for description of seizure scale. Note statistically significantly reduced seizure scores in TRPC5 KO mice at the late phase after pilocarpine injection [P < 0.001, two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)]. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, Bonferroni post hoc tests against WT. (B) Average seizure scores were lower in TRPC5 KO compared with WT mice (P < 0.01, two-way ANOVA). *P < 0.05, Bonferroni post hoc tests against WT. Pooled data (mean ± S.E.M.) was plotted (n = 24, 10, and 18, for WT at 175, 222, and 280 mg/kg pilocarpine, respectively; n = 8, 10, and 14 for TRPC5 KO at 175, 222, and 280 mg/kg pilocarpine, respectively; n = 9, 15, and 19 for TRPC1 KO at 175, 222, and 280 mg/kg pilocarpine, respectively). (C) Mortality in the first 24 hours after pilocarpine injections was reduced in TRPC5 KO mice (n = 8, 10, and 14) compared with WT mice (n = 24, 10, and 18) and TRPC1KO mice (n = 9, 15, and 19).