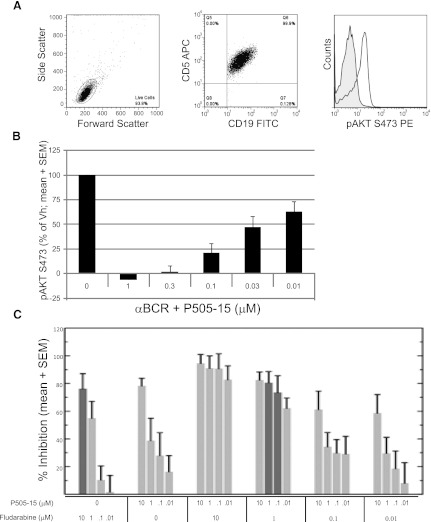
Fig. 5.
P505-15 inhibits BCR mediated signaling, and when combined with fludarabine shows increased cell killing and is fludarabine sparing at nanomolar and low micromolar concentrations. (A) representative BC-mediated AKT phosphorylation in CLL cells as shown by flow cytometry. The left and middle panels depict gating on CD5+/CD19+ CLL cells. The histogram shows a representative (n = 7) induction of AKT S473 following BCR ligation. (B) P505-15 inhibits AKT phosphorylation following BCR ligation of CLL cells in a concentration-dependent manner (mean + S.E.M., n = 7). (C) CLL cells were treated with fludarabine alone, P505-15 alone, or in the combinations indicated. Percent inhibition of viability (mean and S.E.M., n = 13) is plotted on the y-axis. Percent inhibition is P505-15 is dose dependent. The dark gray bars direct attention to cell killing in the presence of 10 µM fludarabine alone (far left bar) relative to 1 µM fludarabine combined with 1 µM or 0.1 µM P505-15 where equivalent cell kill was observed.