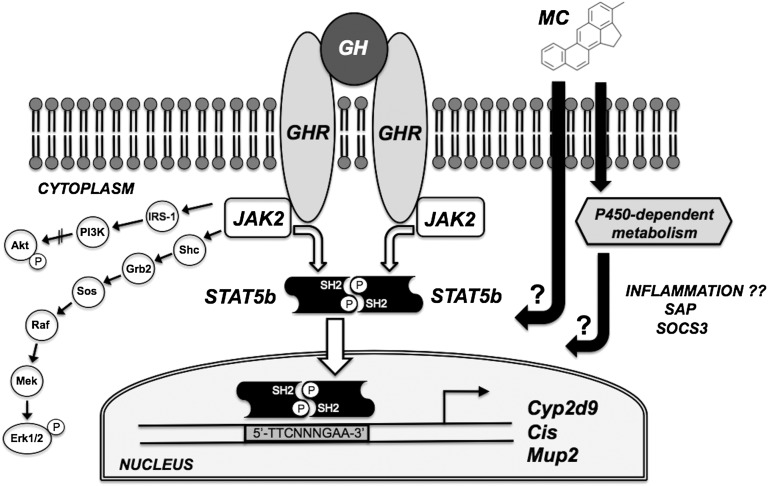
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the potential disruption of hepatic GH signaling pathways by MC. GH triggers dimerization of the cell-surface GHR leading to activation of at least three signal transduction cascades: the GHR-JAK2-STAT5b pathway leading to transcription of STAT5b target genes such as Cyp2d9, Cis, and Mup2; the PI3K pathway leading to phosphorylation of Akt; and a mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade leading to phosphorylation of Erk1/2. MC may disrupt these signaling pathways via P450-dependent or P450-independent mechanisms. MC’s effects may also be accompanied by induction of hepatic inflammatory markers (e.g. SAP and SOCS3). Abbreviations not appearing elsewhere in text: IRS-1, insulin receptor substrate-1; Shc, (Src homology 2 domain containing)-transforming protein; Grb2, growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; Sos, son of sevenless.