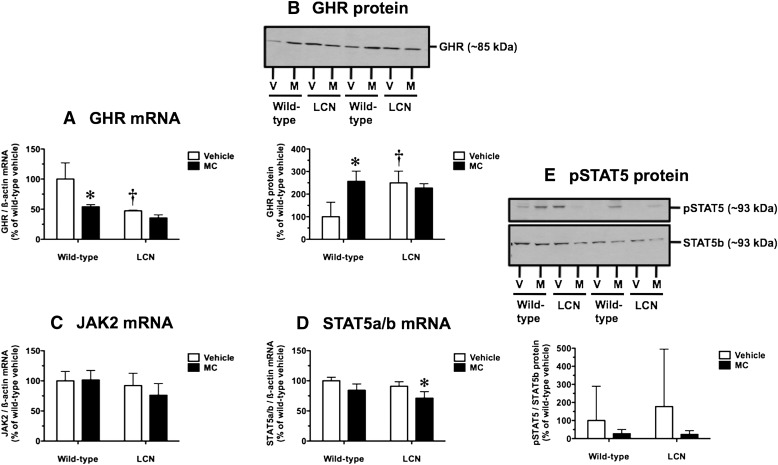
Fig. 6.
Effect of MC treatment on hepatic GHR mRNA (A), GHR protein (B), JAK2 mRNA (C), STAT5a/b mRNA (D), and pSTAT5/STAT5b protein ratio (E) in wild-type and LCN mice. Immunoblot of whole-liver homogenate protein (40 µg) using polyclonal antibody against mouse GHR (B), polyclonal antibody against mouse pSTAT5, and monoclonal antibody against mouse STAT5b (E), showing results for two vehicle (V)- and MC (M)-treated mice per genotype. Quantitative analysis of GHR mRNA (A), JAK2 mRNA (C), and STAT5a/b mRNA (D) levels, relative to β-actin, and GHR protein levels (B) and pSTAT5/STAT5b protein ratio (E). Data represent the mean ± S.D. of determinations from four mice per group, expressed as a percentage of the mean for the vehicle-treated wild-type mice. The P values for the two-way ANOVA main effects were P = 0.0013 (treatment), P = 0.0002 (genotype), and P = 0.0292 (interaction) for GHR mRNA; P = 0.0172 (treatment), P = 0.0280 (genotype), and P = 0.0030 (interaction) for GHR protein; P = 0.4616 (treatment), P = 0.0984 (genotype), and P = 0.3760 (interaction) for JAK2 mRNA; P = 0.0018 (treatment), P = 0.0284 (genotype), and P = 0.6588 (interaction) for STAT5a/b mRNA; and P = 0.2441 (treatment), P = 0.6964 (genotype), and P = 0.6669 (interaction) for pSTAT5/STAT5b protein ratio. Post-test outcomes were as follows: *significantly different (P < 0.05) from genotype-matched vehicle-control mice; †significantly different (P < 0.05) from treatment-matched wild-type mice.