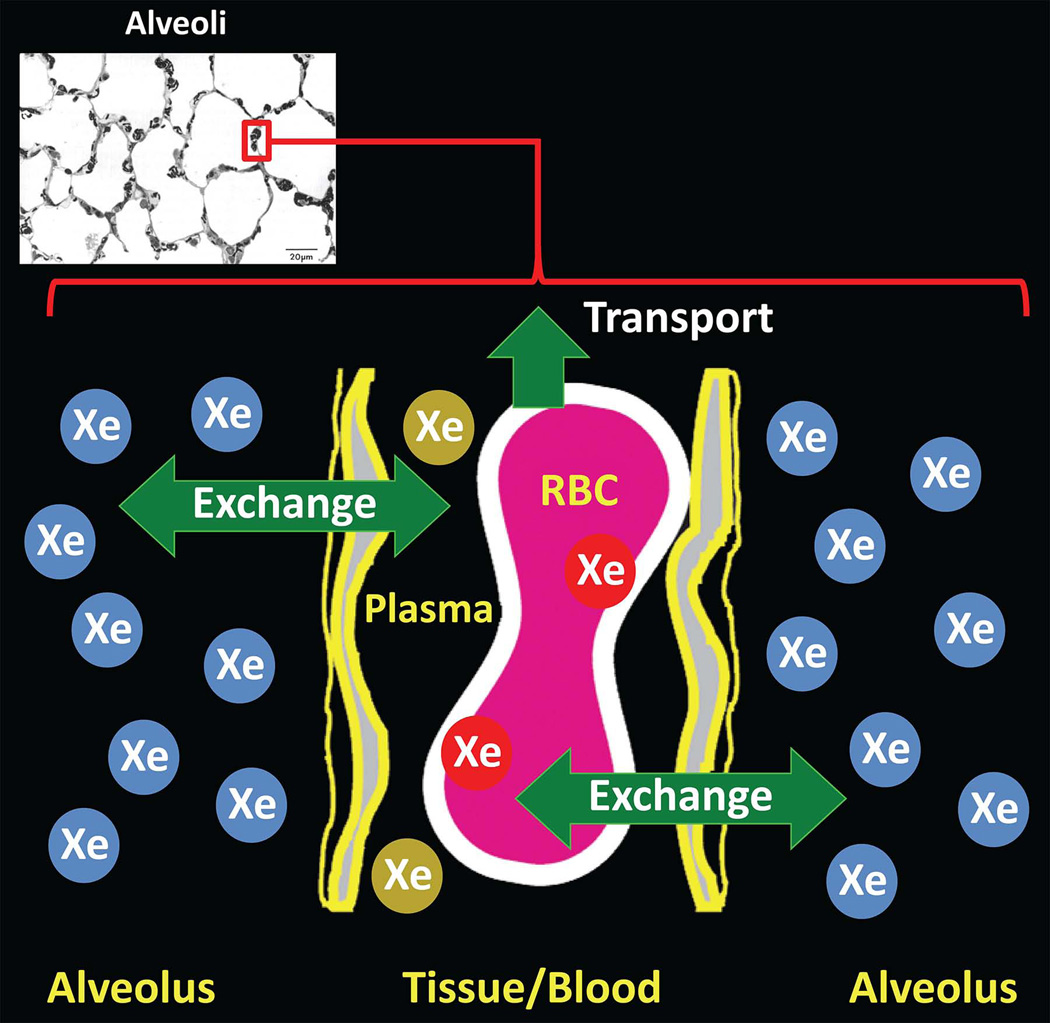
Figure 11.
129Xe exchange between lung airspaces and tissue. Following inhalation, a dynamic equilibrium is quickly established between xenon in the airspaces and xenon dissolved in the parenchyma and blood, resulting in diffusion-driven exchange of xenon between the airspaces (blue Xe atoms) and dissolved-phase compartments (red and gold Xe atoms). A fraction of dissolved xenon is transported to other organs by the bloodstream. (Diagram adapted from Fig. 2 of ref. (20). Micrograph reproduced with permission from Albertine KH. Structural organization and quantitative morphology of the lung. In: Cutillo AG, ed. Application of Magnetic Resonance to the Study of Lung. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell, 1996; 73–114.)