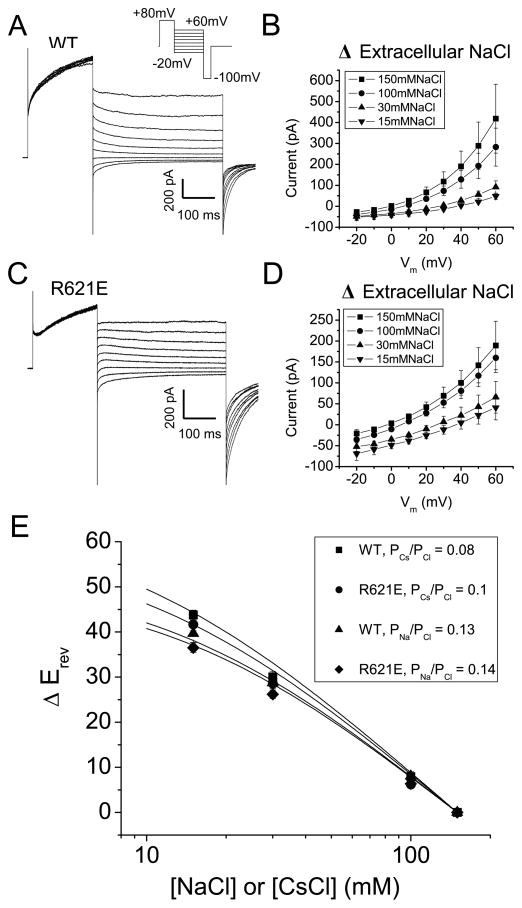
Figure 5.
Effect of R621E mutation on anion:cation permeability of mAno1. (A, B) Whole-cell recordings of (A) WT mAno1 in symmetrical 150 mmol/L NaCl with 180 nmol/L Cai and (B) R621E mAno1 in symmetrical 150 mmol/L NaCl with 1.1 μmol/L Cai. The R621E mutation decreased the Ca2+ sensitivity of the channel, requiring a larger Ca2+ concentration to generate a measurable current. (C, D) Current-voltage relationships of (C) WT mAno1 and (D) R621E mAno1 with different extracellular [NaCl]. (E) Change in reversal potential (ΔErev) for different extracellular [NaCl] or [CsCl] determined from experiments like those in C and D. Lines are best fits to the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation.