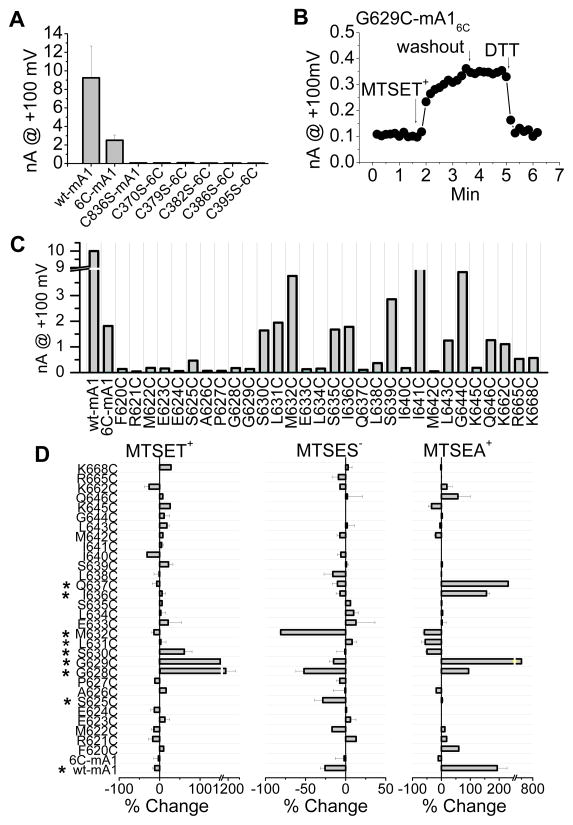
Figure 6.
Essential cysteines in mAno1 and scanning cysteine accessibility of the proposed new TMD6 (amino acids 620–646). (A) Six extracellular cysteines are required for mAno1 function. Amplitudes of whole-cell currents activated by 20μmol/L [Ca2+]i at +100mV from WT and cysteine-substituted mutants of mAno1 expressed in HEK293 cells. Inset shows location of cysteines (solid red circles: essential; open red circles: not-essential for channel function) in the old model of mAno1. 6C: mAno1 with all cysteines except C370, C379, C383, C386, C395 and C836 replaced with serines. C836S is wild type mAno1 with C836 only replaced with serine. The other constructs have each of the essential cysteines in mAno16C as indicated replaced with serine. (B) Example of change in current amplitude of G629C mANO16C. MTSET-induced increase in current is not reversed by washout of MTSET but is reversed by 5 mmol/L DTT. (C) Average Ano1 currents recorded from WT mAno1, mAno16C and cysteine-substituted mAno16C. (D) Effects of MTSET+ (left), MTSES− (middle) and MTSEA+ (right) on cysteine-substituted mAno16C. The percent change of current at +100mV within 2 min of exposure to MTS reagent was calculated by [100 (Iafter MTS − Ibefore MTS)/Ibefore MTS]. Cysteine-substituted amino acids labeled with an asterisk were significantly (p < 0.05) affected by MTS reagents (N= 3–6).