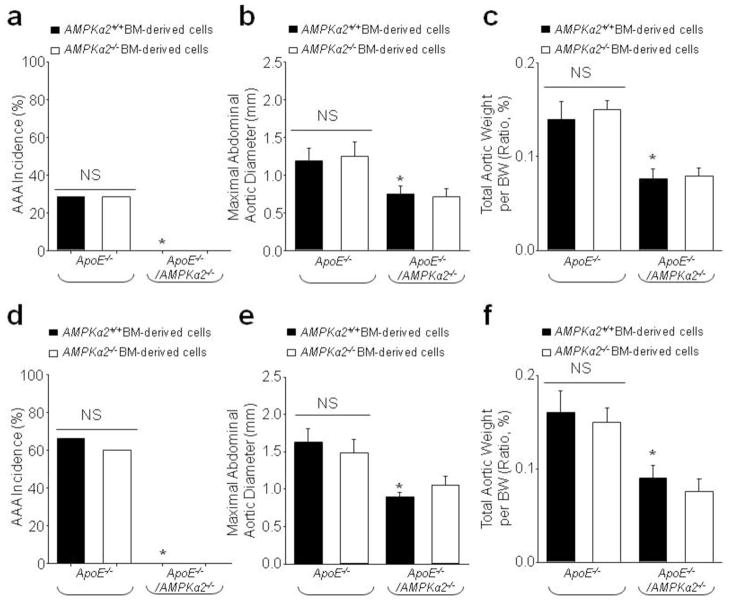
Figure 3.
Bone marrow (BM) reconstitution shows a key role for vascular-specific AMPKα2 deficiency in AAA formation. After irradiation, ApoE−/− and ApoE−/−/AMPKα2−/− mice were immediately injected with BM-derived cells from ApoE−/− and ApoE−/−/AMPKα2−/− mice. (a–c) 6 weeks later, mice were infused with nicotine (1 mg/kg/day) for 6 weeks. (a) The incidence of AAA, (b) Maximal abdominal aortic diameters, and (c) Total aortic weights in nicotine-infused mice. N=10–15 in each group. *P<0.05 vs. nicotine-infused ApoE−/− plus ApoE−/−AMPKα2+/+ BM-derived cells. NS indicates no significant difference. (d–f) 1 week later, mice were infused with AngII (1.44 mg/kg/day) for 4 weeks by using an osmotic pump. (d) The incidence of AAA, (e) Maximal abdominal aortic diameters, and (f) Total aortic weights in AngII-infused mice. N=10–15 in each group. *P<0.05 vs. AngII-infused ApoE−/− plus ApoE−/−AMPKα2+/+ BM-derived cells. NS indicates no significant difference.