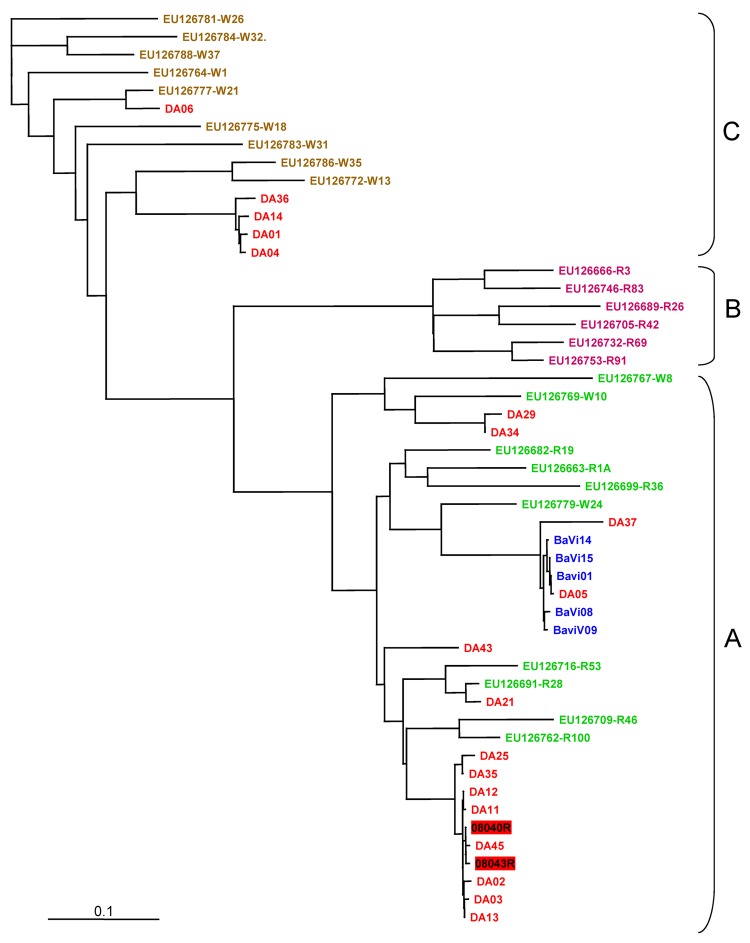
Figure.
Genotyping of human rhinovirus (HRV) from outbreak and control specimens by P1–P2 sequence analysis. We compared 19 HRVs from the outbreak orphanage (red), 5 HRVs from control orphanage blue), and the following P1-P2 sequences in GenBank, according to Lee et al. (3). HRV-A group (green): EU126769, EU126779, EU126767, EU126699, EU126682, EU126663, EU126716, EU126691, EU126709, EU126762; HRVB group (orange): EU126732, EU126689, EU126666, EU126753, EU126705, EU126746, HRV-C group (brown): EU126786, EU126772, EU126775, EU126777, EU126783, EU126788, EU126784, EU126781, EU126764. Two HRV sequences from hospitalized patients were included (HRV number in red box). Multiple sequence alignment was performed by using the BioEdit program package (Ibis Biosciences, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Nucleotide distances were analyzed with DNAdist, the neighbor-joining tree of BioEdit package. The consensus tree was visualized by TREEVIEW v1.6.6 (Institute of Biomedical and Life Sciences, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK). Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.