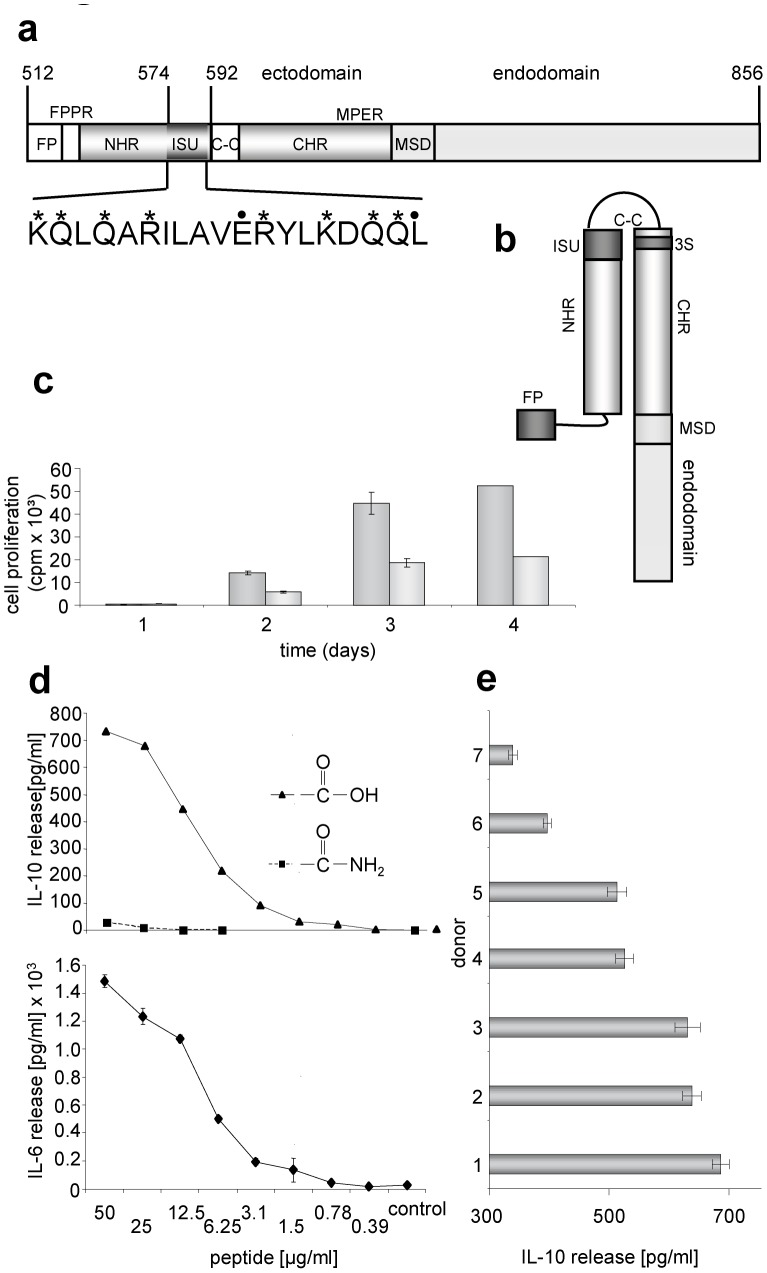
Figure 1. Localisation and activity of the immunosuppressive (isu) domain of gp41 of HIV-1.
(a) Functional domains in gp41 of HIV-1 (accession-nr. NCBI K03455): FP, fusion peptide; FPPR, fusion peptide proximal region; NHR, N-terminal helical region; ISU, isu domain; S-S, cystein-cystein loop; CHR, C-terminal helical region; MPER, membrane proximal external region; MSD, membrane spanning domain, 3S, domain binding to the gC1qR and inducing NKp44L expression. In the amino acid sequence of the isu domain stars (*) indicate NH2-groups, points (.) mark COOH groups relevant for polymerisation. (b) Localisation of the isu domain after interaction of the NHR with the CHR generating a six helix bundle (only one molecule of the trimer is shown). (c) Influence of the isu-peptide on the proliferation of PHA stimulated PBMCs from a healthy donor. Cell proliferation was measured by 3H-thymidine incorporation. 3H-thymidine was added on day zero, one, two or three and cells were then harvested one the next day and the counts per minute were determined, gray - medium control, dark gray – isu peptide-BSA conjugates, added at day 0. (d) Dose dependent induction of IL-6 and Il-10 release by the isu peptide homopolymer (triangle) as measured in ELISAs. In contrast, the amidated control peptide (square) is inactive. (e) Comparative ELISA analysis of IL-10 release from PBMCs of seven donors all treated with the same amount and batch of the isu-peptide homopolymer, the IL-10 release of their PBMCs incubated with medium alone was zero. The p values were calculated using the Student's t-test, n = 3. The p value for the high responder donor 1 was p = 0.001, that of the low responder donor 7 p = 0.03.