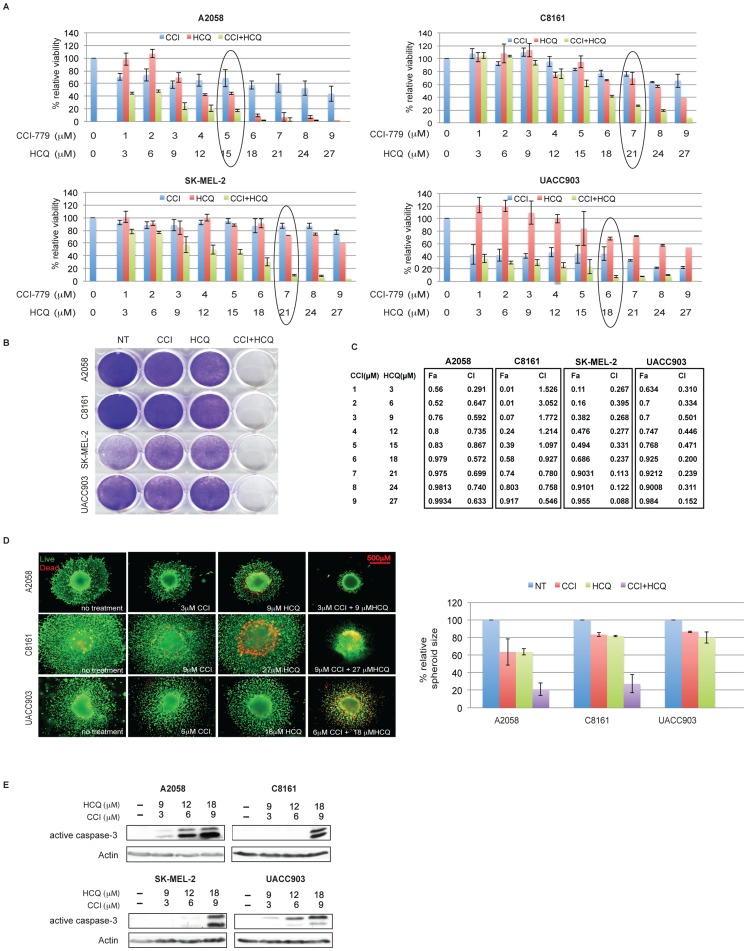
Figure 3. HCQ and CCI-779 synergize to induce melanoma cell death.
(A) Melanoma cells (2×104) were plated in 12 well plates, and treated with CCI-779 and HCQ alone and in combination at the concentrations indicated. The cell viability was examined at day 4 by Trypan blue stain based cell counting and normalized to untreated cells at the time zero. Relative viability showed that CCI-779 and HCQ cooperate to promote cell death. (B) Clonogenic survival assay showed that melanoma cells treated with CCI-779 and HCQ in combination at the concentration as circled in (A) impaired colony formation. (C) Synergistic effects were analyzed by CalcuSyn software, with a fixed ratio of CCI- 779 and HCQ concentration (1∶3) as indicated. Experimental points fall mostly below the borderline (CI = 1) indicating strong synergism. (D) Inhibition of melanoma cell growth in three-dimensional culture. Melanoma cell spheroids were grown as described in the Materials and Methods. After 72 hours of incubation with CCI-779 and HCQ alone and in combination, the cells were treated with cell LIVE/DEAD Viability kit wherein living cells stain green and dead cells stain red. Representative 3-D spheroid pictures showed synergism between CCI-779 and HCQ (scale bar = 500 µM) (left), with the graph at right displaying the percentages of spheroid diameters (mean ± SD) normalized to the untreated spheroids. Spheroids of UACC903 disintegrated after the treatment. (E) Combination HCQ and CCI-779 induced cell death via apoptosis. Western blot of melanoma cells treated with HCQ and CCI-779 at indicated concentrations demonstrated increased active caspase-3 indicating apoptotic cell death.