Figure 3. Overlay of fiber tracts identified for more difficult (red) and easier (blue) mental arithmetic.
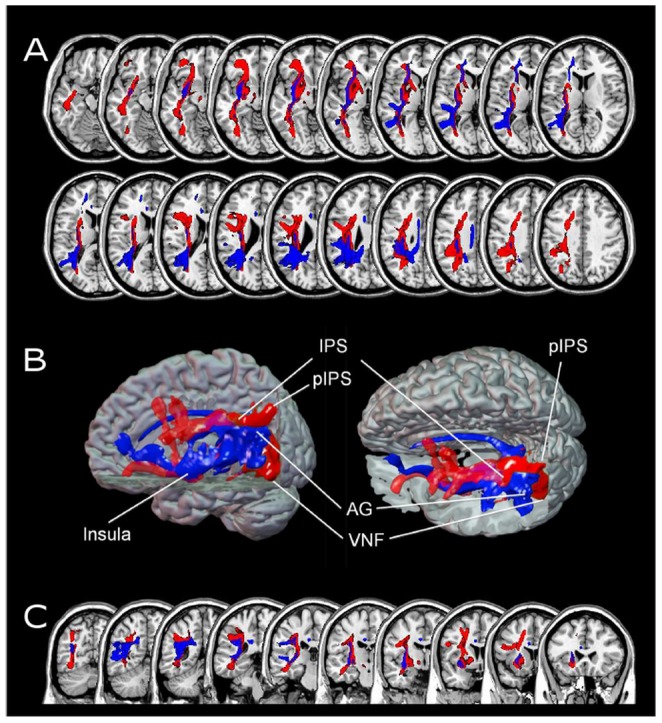
Panel A gives a detailed view on the course of the fiber tracts in axial orientation. Two largely anatomically distinct dorsal vs. ventral fiber pathway profiles for the processing of more difficult (magnitude-related) and the easier (fact retrieval related) problems can be observed. Importantly, difficult mental arithmetic (depicted in red) and easier mental arithmetic (depicted in blue) seems to involve two largely separate networks differing not only in localization of activation but also in the connections between associated cortex areas. Additionally, the connection between the visual number form area (VNF) and the number magnitude representation (IPS/pIPS) is displayed in red. Panel B again reflects the identified pathways in a 3D volume rendering with PIBI values>0.0148. Finally, Panel C depicts a detailed view on the course of the fiber tracts in coronal orientation, illustrating that easier mental arithmetic encompasses the EC/EmC system more superiorly and medially (depicted in blue), whereas more difficult mental arithmetic recruits more inferior and lateral components of the EC/EmC system (depicted in red).Abbreviations: AG = angular gyrus; IPS = intraparietal sulcus; pIPS = posterior intraparietal sulcus; VNF = visual number form.
