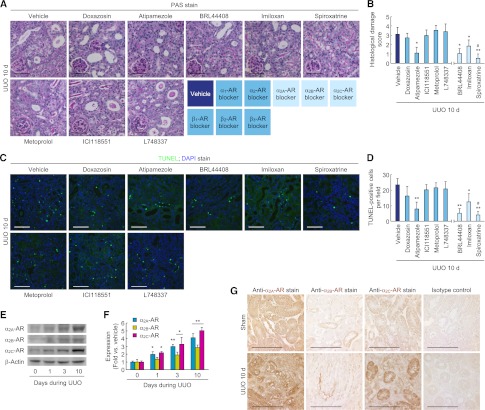
Figure 6.
α2-AR antagonists reduce tubular cell death and are upregulated after UUO. (A–D) Male 129S1/SvImJ mice aged 8–10 weeks were continuously treated with doxazosin (α1-AR antagonist, 12 mg/kg per day), atipamezole (α2-AR antagonist, 2.4 mg/kg per day), metoprolol (β1-AR antagonist, 12 mg/kg per day), ICI118551 (β2-AR antagonist, 2.4 mg/kg per day), L748337 (β3-AR antagonist, 2.4 mg/kg per day), BRL44408 (α2A-AR antagonist, 12 mg/kg per day), imiloxan (α2B-AR antagonist, 12 mg/kg per day), spiroxatrine (α2C-AR antagonist, 12 mg/kg per day), or vehicle (10% DMSO in PBS) via an intraperitoneal implantation of a mini-osmotic pump 24 hours before UUO (n=5). (A) Histologic damage indicated by PAS staining in UUO kidneys treated with AR antagonists. (B) The histologic damage was scored by counting the percentage of tubules. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus vehicle; #P<0.05 versus imiloxan. (C) TUNEL assay to detect apoptotic cells in UUO kidneys treated with AR antagonists using In Situ Cell Death Detection kit. The visible blue color indicates nuclei stained by DAPI. (D) The number of TUNEL-positive apoptotic cells in tubules was counted in five randomly chosen high-power (×200) fields per kidney. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus vehicle; #P<0.05 versus imiloxan. (E–G) Left ureters of male 129S1/SvImJ mice aged 8–10 weeks were obstructed for 0, 1, 3, or 10 days (n=4). (E and F) α2A-AR, α2B-AR, and α2C-AR expression using Western blot analysis. Anti–β-actin antibody served as a loading control. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus 0 days. (G) Immunohistochemistry of α2A-AR, α2B-AR, and α2C-AR in UUO or sham kidneys. Scale bar, 50 μm. Error bars represent SDs.