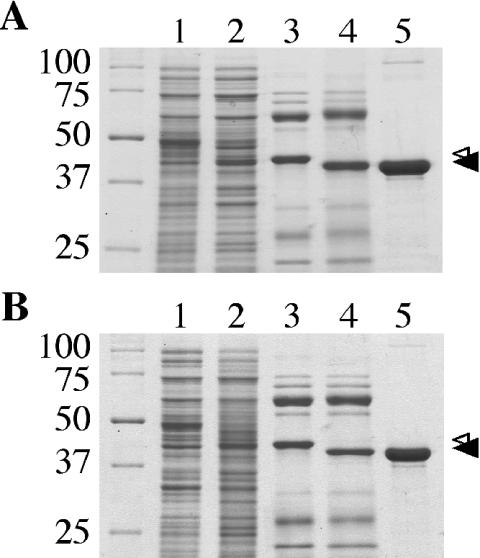
FIG. 2.
Purification of DotB and DotB K162Q from E. coli. (A) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel showing wild-type DotB purification steps. Lane 1, cell extract from E. coli C600 containing plasmid pJB1572, no induction; lane 2, cell extract from C600(pJB1572), IPTG induced; lane 3, eluate from Ni-NTA-agarose after incubation with His-DotB lysate; lane 4, Ni-NTA eluate after exposure to thrombin; lane 5, purified DotB after three additional separation procedures. (B) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel showing DotB K162Q purification steps. Lanes are as for panel A, except that DotB K162Q was expressed with C600(pJB2442). (A and B) Small arrowhead, His-DotB or His-DotB K162Q bands; large arrowhead, bands representing DotB or DotB K162Q with the His tags removed. Standards of known molecular masses (kilodaltons) are on the left.