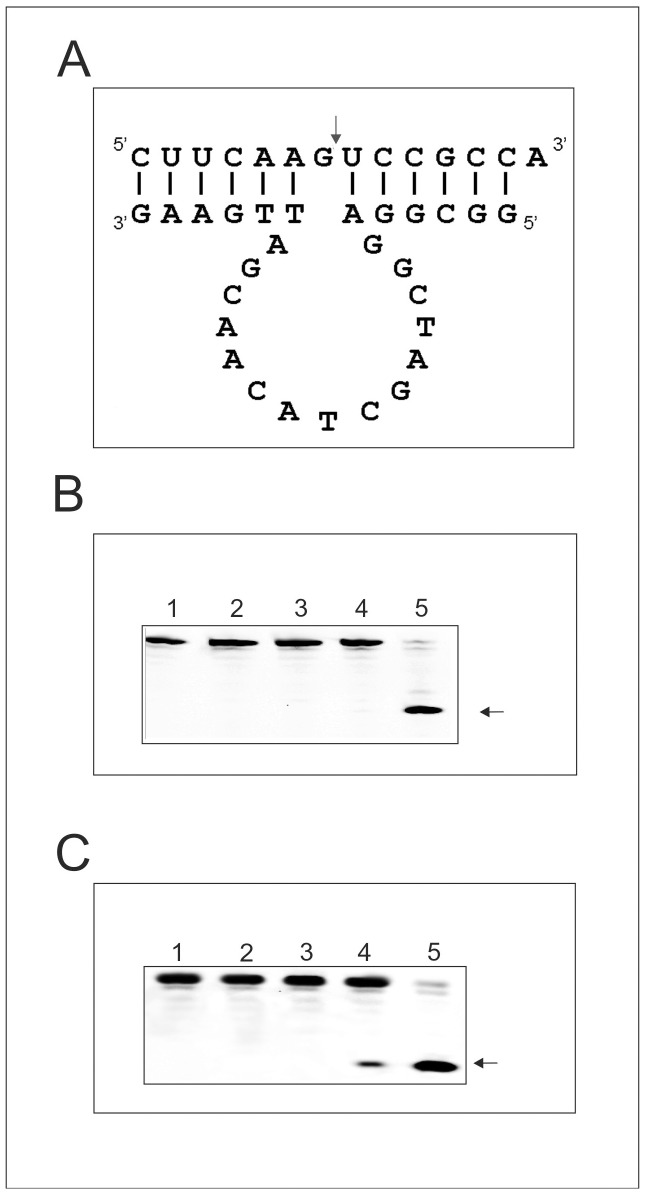
Figure 6. D- or L-RNA2 Hydrolysis by D- or L-DNAzyme.
The general secondary structural model for the D- or L-DNAzyme 10/23 (A), in complex with a D- or L-RNA2 substrate (B). Hydrolysis of D-RNA2 with D-DNAzyme at 10 mM MgCl2. Lanes 1: D-RNA2 incubation in water, lane 2: D-RNA2 incubation in 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5 buffer, lane 3: D-RNA2 incubation in the buffer containing in addition 10 mM MgCl2; lane 4: D-RNA2 hydrolysis with D-DNAzyme in buffer in the absence of MgCl2; lane 5: D-RNA2 hydrolysis with D-DNAzyme in buffer in the presence of 10 mM MgCl2 (C). L-RNA2 hydrolysis with L-DNAzyme at 10 mM MgCl2, analyzed with 20% PAGE with 7 M urea. Lanes 1: L-RNA2 incubation in water, lane 2: L-RNA2 incubation in 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5 buffer, lane 3: L-RNA2 incubation in buffer containing in addition 10 mM MgCl2, lane 4: hydrolysis of L-RNA with L-DNAzyme in the absence of MgCl2; lane 5: hydrolysis of L-RNA substrate with L-DNAzyme in presence of 10 mM MgCl2, All incubations were carried out for 3 hrs and analyzed with 20% PAGE with 7 M urea. Arrows show the specific cleavage site in the D- and L- RNA2 targets.