Figure 3. Molecular mechanism of anti-inflammation by adenosine.
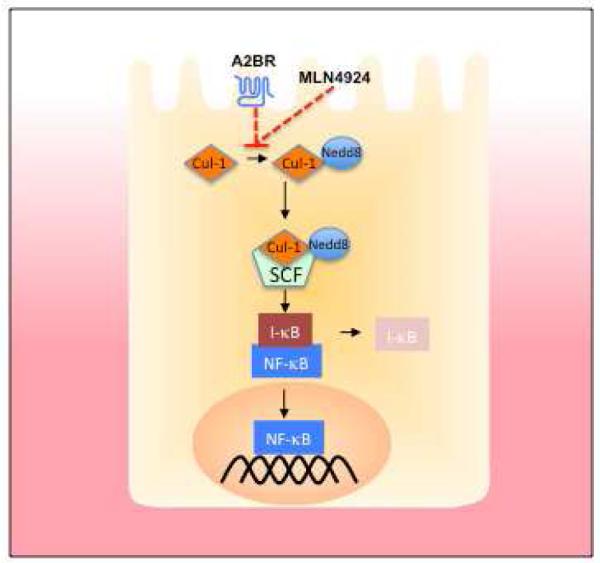
The canonical NFκB pathway is activated through the phosphorylation of IκB. This phosphorylation allows for its recognition by the neddylated Skp-Cullin-F-Box (SCF) complex, polyubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation. Neddylation of Cul-1 is achieved through a multienzyme process, conjugating a NEDD8 moiety to the target protein (see text). Adenosine receptor activation, as well as the neddylation inhibitor MLN4924, inhibit Cullin neddylation or promote deneddylation of Cullin-proteins, thereby inhibiting the overall function of the SCF complex.
