Fig. 3.
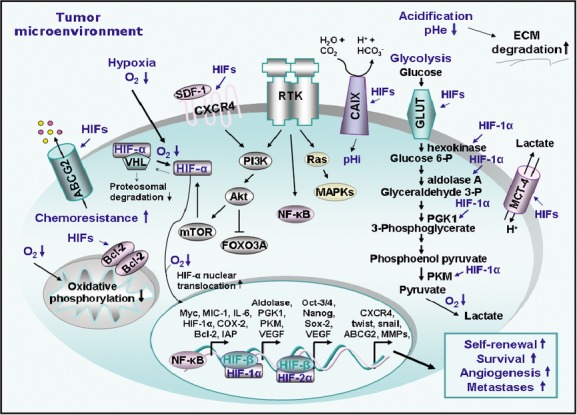
Scheme showing the potential molecular events induced in cancer cells in the hypoxic tumour microenvironment. The intracellular consequences of decreased oxygen level (hypoxia) in cancer cells including the switch of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation to anaerobic glycolysis and enhanced nuclear translocation of HIF-α subunit are illustrated. The enhanced stabilization and activation of HIF-1α and HIF-2α and their formation of nuclear heterodimers with HIF-β receptor in cancer cells under hypoxia that in turn may result in the transcriptional activation of numerous gene products involved in anaerobic glycolysis, pH regulation, self-renewal, survival and induction of angiogenic switch and metastases are indicated. The enhanced cellular accumulation and activation of HIF-α protein subunit which may be induced through the stimulation of different receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) in cancer cells under normoxic and hypoxic conditions are also illustrated. Particularly, the stimulation of RTKs may lead to the sustained activation of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase (PI3K)/Akt/molecular target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway that in turn may induce the translational machinery and HIF protein synthesis and/or enhanced stabilization of HIF-α subunit. Moreover, the activation of RTKs may result in the stimulation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) that in turn can induce the transcriptional up-regulation of HIFs. ABCG2/BCRP: breast cancer resistance protein; CAIX: carbonic anhydrase IX; COX-2: clyooxygenase-2; ECM: extracellular matrix; FOXO3A: forehead 3A; GLUT: glucose transporter; HIFs: hypoxia-inducible factors; IAP: inhibitor of apoptosis protein; IL-6: interleukin-6; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; MCT: monocarboxylate transporter; MIC-1: macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1; MMPs: matrix metalloproteinases; pHe: extracellular pH; pHi: intracellular pH; PGK1: phosphoglycerate kinase 1; PKM: pyruvate kinase M; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor.
