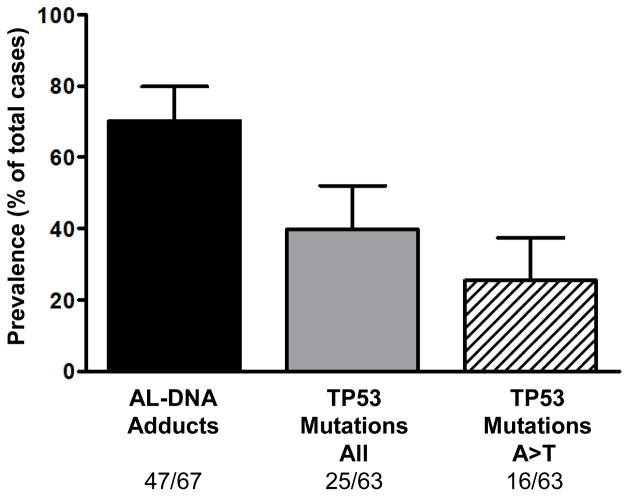
Figure 1.
Prevalence of biomarkers of aristolochic acid (AA) exposure and TP53 mutations in cases of UUC from endemic villages/regions in Bosnia, Croatia and Serbia. Aristolactam (AL)-DNA adducts, produced during intracellular nitroreduction of AA, were measured in renal cortex by a 32P-postlabeling-PAGE assay (43). Specific mutations in the tumor suppressor gene TP53 were identified in UUC samples using p53 AmpliChip technology. A:T T:A transversions (A>T) are the dominant TP53 mutations associated with AA exposure in UUC (16). Tumor DNA was not available for analysis for four cases. Error bars denote 95% confidence intervals for each value. Cortical adducts and tumor TP53 mutations were not detected in DNA samples obtained from nonendemic cases (n=10; data not shown).