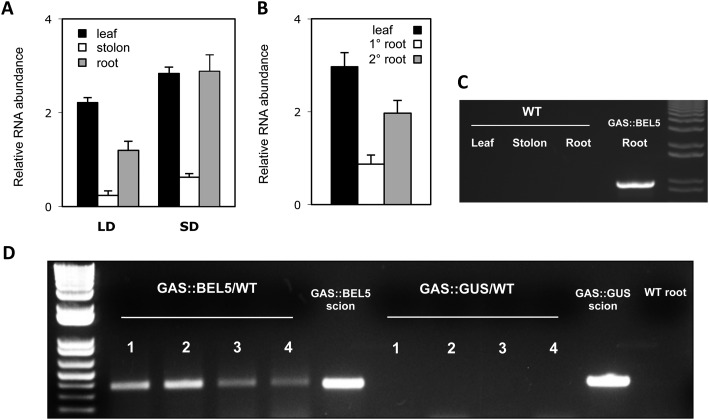
Figure 1.
Movement of transgenic StBEL5 mRNA from leaf to stolon or root. A, Quantification of movement was performed on transgenic lines expressing full-length StBEL5 RNA driven by the GAS promoter of melon (Cucumis melo). This promoter is predominantly expressed in the minor veins of leaf mesophyll (Ayre et al., 2003; Banerjee et al., 2009). Relative levels of transgenic StBEL5 RNA were quantified from total RNA extracted from new leaves (black bars), 0.5-cm samples from the tip of the stolon (white bars), and root samples (gray bars). B, In a separate experiment, relative levels of transgenic StBEL5 RNA were quantified from total RNA extracted from new leaves (black bars) and from either primary (white bars) or secondary (gray bars) root samples of a short-day (SD)-grown GAS:BEL5 transgenic plant. One-step RT-PCR was performed using 200 to 250 ng of total RNA, a primer for the NOS terminator sequence specific to all transgenic RNAs, and a gene-specific primer for the full-length StBEL5 transcript. These primers specifically amplify only transgenic BEL5 RNA. All PCRs were standardized and optimized to yield product in the linear range. Homogenous PCR products were quantified by using ImageJ software (Abramoff et al., 2004) and normalized by using 18S rRNA values. se values of three replicate samples are shown. LD, Long days. C, The specificity of the transgenic primers used in A and B was verified on RNA from wild-type potato ssp. andigena leaf, stolons, and roots using the same PCR conditions. D, For heterografts, micrografts were performed with replicates of either GAS:BEL5 scions on wild-type andigena stocks or GAS:GUS scions on wild-type andigena stocks. After 2 weeks in culture, grafts were moved to soil and grown under long days for 3 weeks and then under short days for 2 weeks before harvest of roots and leaves. After RNA extraction, RT-PCR with gene-specific primers was performed on RNA from wild-type lateral roots of both heterografts. A second PCR was performed with nested primers for both types. RNA from scion leaf samples was used as a positive control (scion samples). Two different gene-specific primers were used with a nonplant sequence tag specific for the transgenic StBEL5 RNA to discriminate from the native RNA. Four plants were assayed for both heterografts and are designated 1 to 4. Wild-type RNA from lateral roots of whole plants (andigena) was used in the RT-PCR, with StBEL5 transgenic gene-specific primers as a negative control (WT root). Similar negative results were obtained with RNA from wild-type leaves.