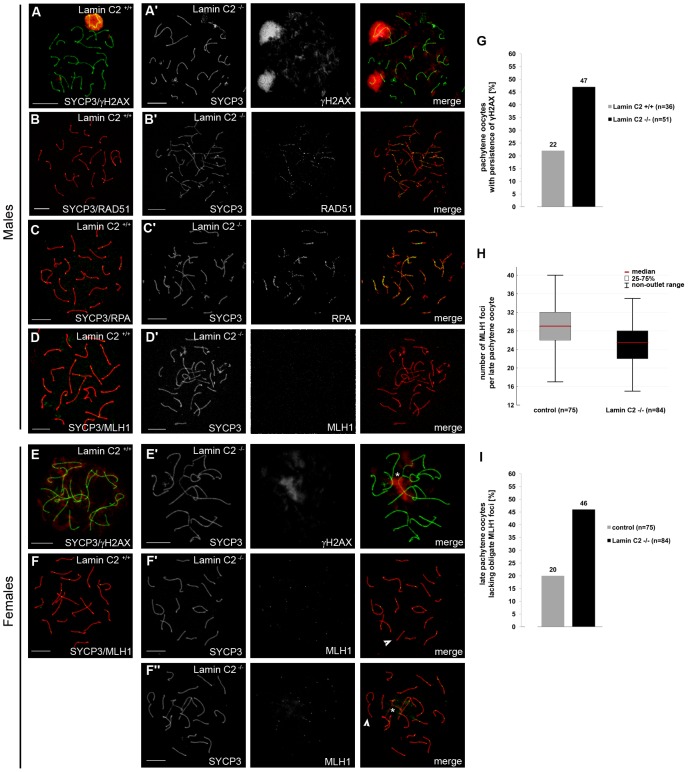
Figure 5. Alterations of meiotic DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair and inefficient homologous recombination caused by lamin C2 deficiency.
Chromosome spread preparations were double-stained using anti-SYCP3 antibodies in combination with anti-γH2AX (A,E), anti-RAD51 (B), anti-RPA (C) or anti-MLH1 (D,F) antibodies. (A–D) In males, lamin C2−/− spermatocytes show incomplete repair of induced DSB as demonstrated by the increased persistence of γH2AX (A′), RAD51 (B′) and RPA (C′) and they lack crossing over events indicated by the complete absence of MLH1 (D′). (E) In females, efficient DSB repair is also affected in lamin C2-deficient pachytene oocytes (17.5 dpf) as revealed by intensive γH2AX staining surrounding incompletely synapsed chromatin (asterisk in E′). (F) In contrast to males, lamin C2−/− females are able to recruit MLH1 onto chromosome axes in 19.5 dpf late-pachytene oocytes. However, the MLH1 foci number was lowered and a significant portion of cells lacked at least one obligate MLH1 focus indicating the absence of cross over recombination on the affected chromosomes (arrowheads in F′ and F″). This phenomenon was likewise seen in oocytes with (asterisk in F″) or without (F′) obvious synaptic defects. Scale bars 10 µm. (G) Quantification of pachytene oocytes with persistence of γH2AX in wildtype and knockout littermates reveals inefficient DSB repair in lamin C2-deficient cells (Pearson's Chi2 test p-value = 0.0323). (H) Whisker box plot showing the number of MLH1 foci per cell in late pachytene oocytes of lamin C2−/− and control (lamin C2+/+ and lamin C2+−/) animals. Two pairs of littermates were analysed. Knockout oocytes show a significant reduction of MLH1 foci number, indicating a lowered rate of homologous recombination (median foci numbers: control, 29; lamin C2−/−, 25.5; Mann-Whitney U-test p-value = 0.00025). (I) The number of late pachytene oocytes lacking one or more obligate MLH1 foci is significantly elevated in lamin C2−/− animals compared to the controls (lamin C2+/+ and lamin C2+/−). As above, two pairs of littermates were analysed (Pearson's Chi2 test p-value = 0.0005).