Table 4. Association between Campylobacter and weight gain.
| Weight Gain (grams/3months) | |||
| Model 1 | Model 2 | ||
| Campylobacter category | No Campylobacter detected | ref | ref |
| Asymptomatic Campylobacter | −65.5** | −67.7** | |
| (−128.0, −3.0) | (−130.1, −5.2) | ||
| Symptomatic Campylobacter, overall | −43.9** | N/A | |
| (−87.6, −0.1) | |||
| Symptomatic Campylobacter, untreated | N/A | −11.0 | |
| (−60.4, 38.5) | |||
| Symptomatic Campylobacter, treated | N/A | −167.2*** | |
| (−267.4, −67.0) | |||
| Non- Campylobacter diarrhea | −22.7*** | −22.9*** | |
| (−35.3, −10.1) | (−35.4, −10.4) | ||
*significant at the p< = 0.10 level.
significant at the p< = 0.05 level.
significant at the p< = 0.01 level.
Weight models adjusted for stunting at onset of interval, WHZ category at onset of interval, season, age, birth weight and per capita income.
Fractional polynomial age term 1: 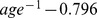 ; age term 2:
; age term 2: 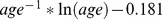 where age is the child's age, in days, divided by 1000.
where age is the child's age, in days, divided by 1000.
In model 1, Campylobacter-related variables were asymptomatic Campylobacter, and symptomatic (diarrhea-associated) Campylobacter (2 variables).
In model 2, Campylobacter-related variables were asymptomatic campylobacter, symptomatic treated campylobacter, and symptomatic untreated campylobacter (three variables).
