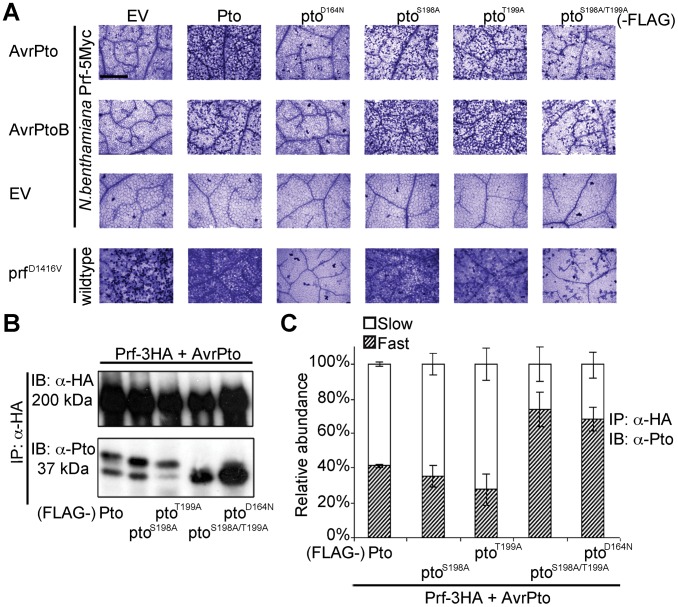
Figure 2. Phosphorylation on Pto residues S198 and T199 is required for signalling.
(A) Trypan blue staining of cell death in N. benthamiana leaves. Pto-FLAG, pto mutant-FLAG, AvrPto, AvrPtoB, and prfD1416V-3HA constructs were transiently expressed in ProPrf:Prf-5Myc or wild-type N. benthamiana as indicated and the tissue was stained 2 days post infiltration. The bar indicates 0.5 mm. Dead cells stain dark blue in this qualitative assay. Each row is derived from a single leaf, within which relative amounts of cell death were comparable, and is representative of six replicates. (B) The slow-migrating form of Pto requires kinase activity and double phosphorylation. Pto-FLAG, pto mutant-FLAG, AvrPto, and Prf-3HA constructs were transiently expressed in wild-type N. benthamiana as indicated, Prf-3HA was immunoprecipitated (IP) using anti-HA antibodies. Immunoblots (IB) were performed with the antibodies indicated on the left. (C) Quantification of the relative abundance of slow- and fast-migrating forms of Pto under elicitation conditions as described in B with Quantity One, Bio-Rad (adjusted volume = [CNT*mm2] data counts/mm2). Error bars are standard deviation of relative abundance between the same samples in independent immunoblots, probed with anti-Pto antibody.