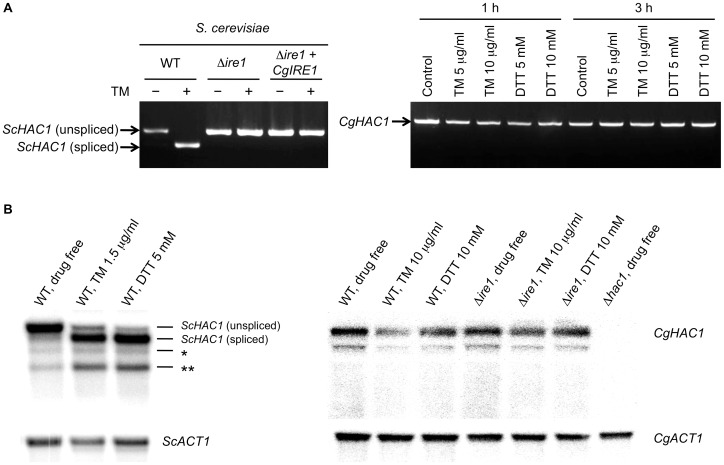
Figure 4. Assays for HAC1 mRNA splicing.
(A) RT-PCR analysis. The S. cerevisiae strains containing either empty vector or pRS415-ADH-CgIRE1, in which C. glabrata IRE1 was expressed under the control of the S. cerevisiae ADH1 promoter, were incubated in SC-leu broth in the presence and absence of 1.5 µg/ml tunicamycin (TM) for 3 h. S. cerevisiae strains: WT, BY42-1; Δire1, BY42I-1; and Δire1+CgIRE1, BY42I-2. The C. glabrata wild-type strain CBS138 was incubated in SC broth in the presence and absence of TM and dithiothreitol (DTT) at the indicated concentrations for 1 and 3 h. RT-PCR products of the entire HAC1 mRNA in S. cerevisiae (left panel) and C. glabrata (right panel) were electrophoresed on a 1% agarose gel. (B) Northern blot analysis. S. cerevisiae WT (BY4742) cells were treated with 1.5 µg/ml TM or 5 mM DTT for 1 h (left panel). C. glabrata cells were treated with 10 µg/ml TM or 10 mM DTT for 3 h (right panel). Both ScHAC1 and CgHAC1 probes were generated from the 5′ regions of the HAC1 ORFs. The same blot was probed for HAC1 mRNA, stripped, and then probed for ACT1 mRNA. The asterisks indicate potential splicing intermediates (*: 5′ exon plus the intron; **: 5′ exon alone). C. glabrata strains: WT, CBS138; Δire1, TG121; and Δhac1, TG141.