Figure 7. The 11R-VIVIT peptide inhibitor of NFATs decreases bacterial phagocytic killing capacity by neutrophils and increases renal susceptibility to UPEC.
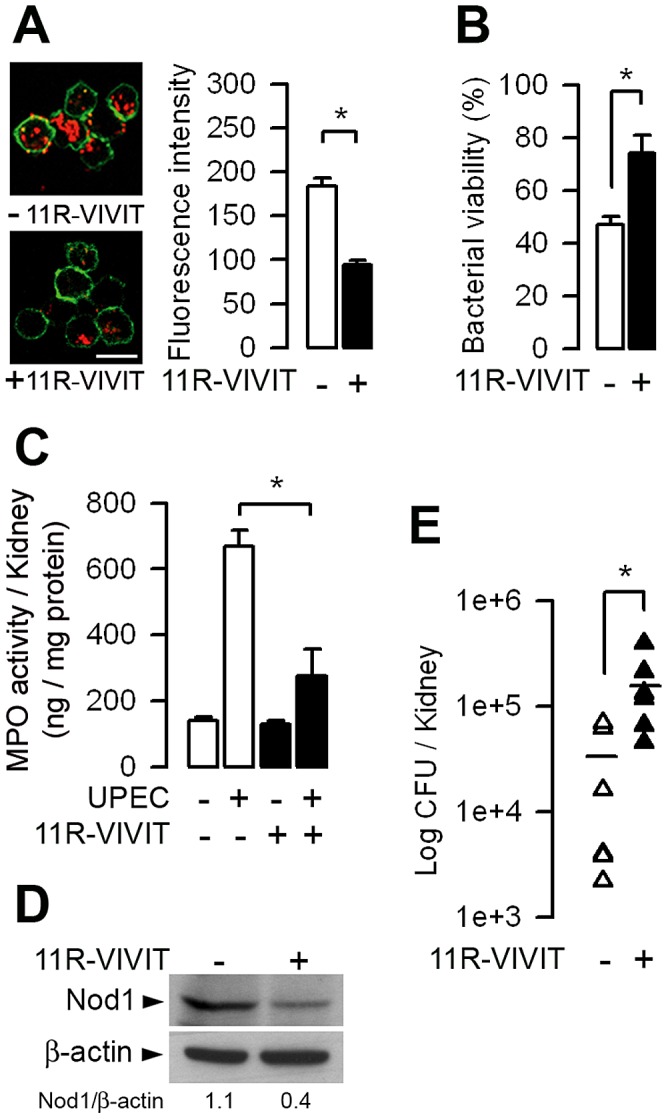
WT mice were given daily intraperitoneal injections of 10 µg/kg 11R-VIVIT for 48 h before the transurethral inoculation of UPEC. (A) Illustrations and quantification of internalized Texas red-coupled E. coli by peritoneal neutrophils from untreated (−) and 11R-VIVIT-treated (+) mice. Values are represented as mean ± SE of the mean count values (2–4 per condition) from three independent experiments. Cell membranes were stained with CD11b-FITC. Bars = 10 µm. (B) Killing of serum-opsonized E. coli by peritoneal neutrophils from untreated and 11R-VIVIT-treated mice. Bacterial viability was expressed relative to control assay performed without neutrophils (n = 3–5 determinations from 3 experiments). (C to E) MPO activity (C), representative immunoblot analysis of Nod1 and corresponding ß-actin (D), and bacterial counts (E) in kidneys from untreated and 11R-VIVIT-treated WT mice 24 h after UPEC inoculation. The numbers indicate the ratio of Nod1 over ß-actin densitometric values from 4 experiments and the horizontal bars show the mean of bacterial counts of each group (n = 6 determinations in each group). Values are presented as mean ± SE. *, p<0.05 between groups (Two-tailed, unpaired Student's t test).
