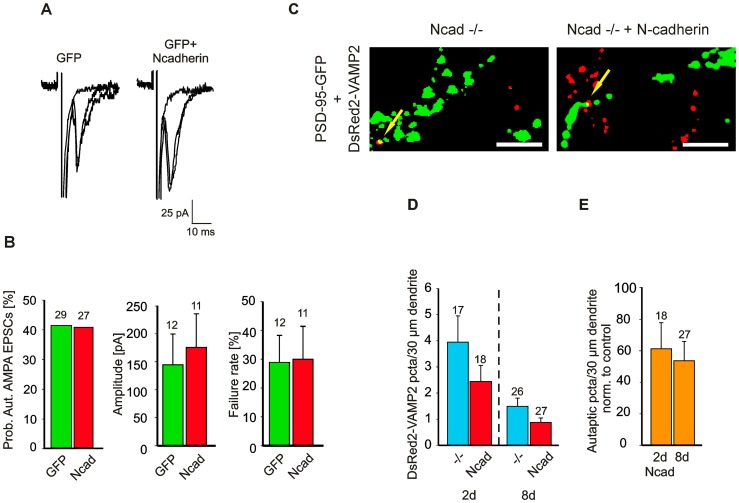
Figure 3. Symmetric, pre- and postsynaptic expression of N-cadherin at autapses does not impair synaptic function.
(A) Autaptic AMPA EPSCs recorded from N-cadherin knockout neurons transfected with either EGFP (GFP) or N-cadherin+EGFP (GFP+N-cadherin, Ncad). Autaptic AMPA EPSCs were elicited by action currents induced by depolarizing pulses in the same neuron. Holding potential −60 mV. 3 traces superimposed. Stimulation artefacts and Na+ currents are truncated. (B) Quantification of autaptic AMPA EPSCs. Left: Probability of occurrence of autaptic AMPA EPSCs (5mM Ca2+). 11–13 DIV, 2 days after transfection. Center: Peak amplitudes. Right: Failure rates. (C, D, E) Incidence of autapses is not significantly affected in N-cadherin knockout neurons expressing N-cadherin. (C) Autapses were identified by coexpression of DsRed2-VAMP2 and PSD-95-EGFP in N-cadherin knockout neurons (Ncad−/−, control) and in N-cadherin knockout neurons expressing N-cadherin (Ncad−/− + N-cadherin). Overlays of corresponding DsRed2-VAMP2 (red) and PSD-95-EGFP (green) fluorescence images (8 days after transfection; 22 DIV, same cells as in Fig. 2B) that were strongly thresholded to visualize the rare autapses (arrows). Scale bars: 2,5 µm. (D) Quantification of dendritic density of DsRed2-VAMP2 puncta (autapses) 2 days (2d) and 8 days (8d) after transfection at 14 DIV. −/−: N-cadherin knockout neurons. Ncad: N-cadherin knockout neurons expressing N-cadherin. Same cells as in Fig. 2. Note the strong (non-significant) trend to a general reduction in the number of autapses with time in culture. (E) No significant changes in the dendritic density of glutamatergic autapses (colocalized DsRed2-VAMP2 puncta and PSD-95-EGFP puncta) were induced by N-cadherin expression (Ncad). Normalized to values of N-cadherin knockout neurons (control) at matched times in culture. Means ± SEM. n (cells) is indicated on bars. Students t-test, ANOVA (D).