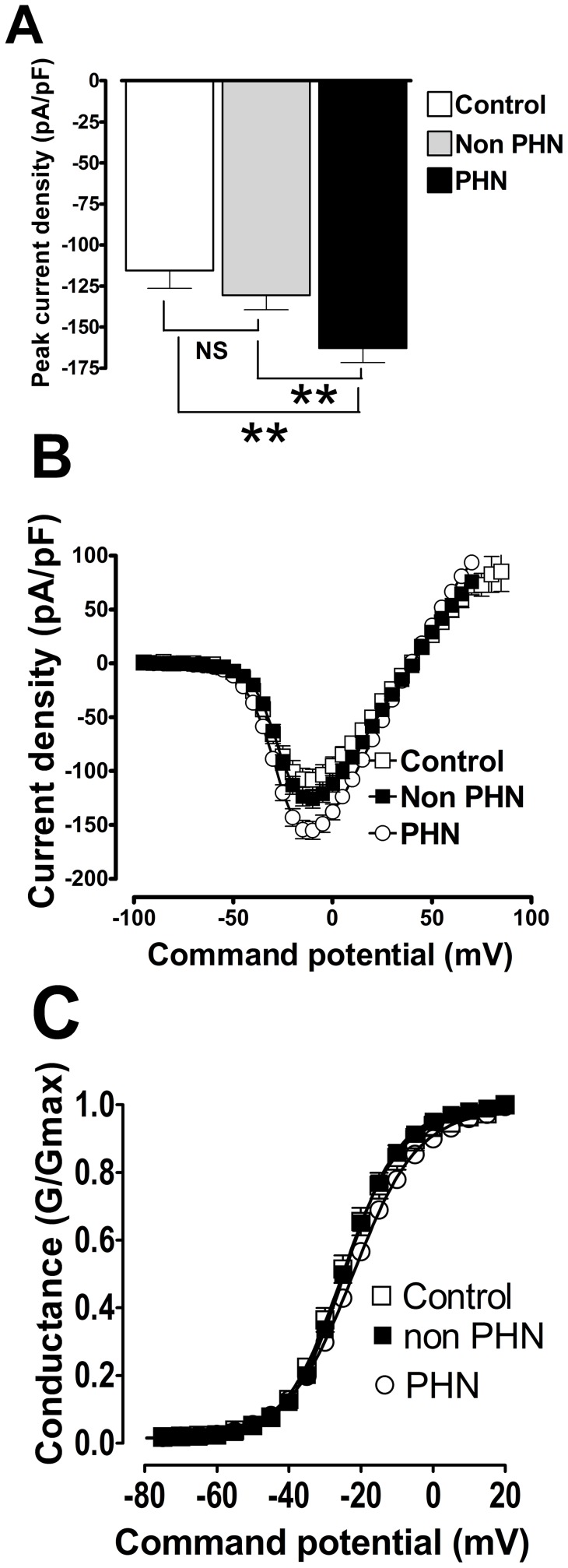
Figure 3. VZV isolates implicated in post herpetic neuralgia significantly increase sodium current density in ND7-23 1.8 cells.
(A) Comparison of peak current densities in sham treated control cells (solid black bar), cells exposed to VZV isolates not implicated in post herpetic neuralgia (non PHN; solid grey bar) and cells exposed to VZV isolates implicated in post herpetic neuralgia (PHN, open bar) (**p<0.01, Analysis of Variance Newman-Keuls multiple comparison post hoc test). (B) Conventional current density verses membrane potential plots for sodium currents from sham treated control cells (open squares) and cells exposed to viral isolates non-PHN (black squares) and PHN VZV isolates (open circles). Data was generated using the following protocol: VHold = −120 mV to +100 mV depolarized in 5 mV increments for 25 ms every 1 sec. (C) Data from (B) represented as a conductance plot. Lines were generated and fitted using a standard Boltzman function that yielded similar half maximal activation voltages (V½ control = −23.5±1.3 mV; V½ nonPHN = −22.7±0.9 mV and V½ PHN = −22.9±0.7 mV) showing that VZV isolates do not significantly alter the voltage-dependence of sodium channel activation.