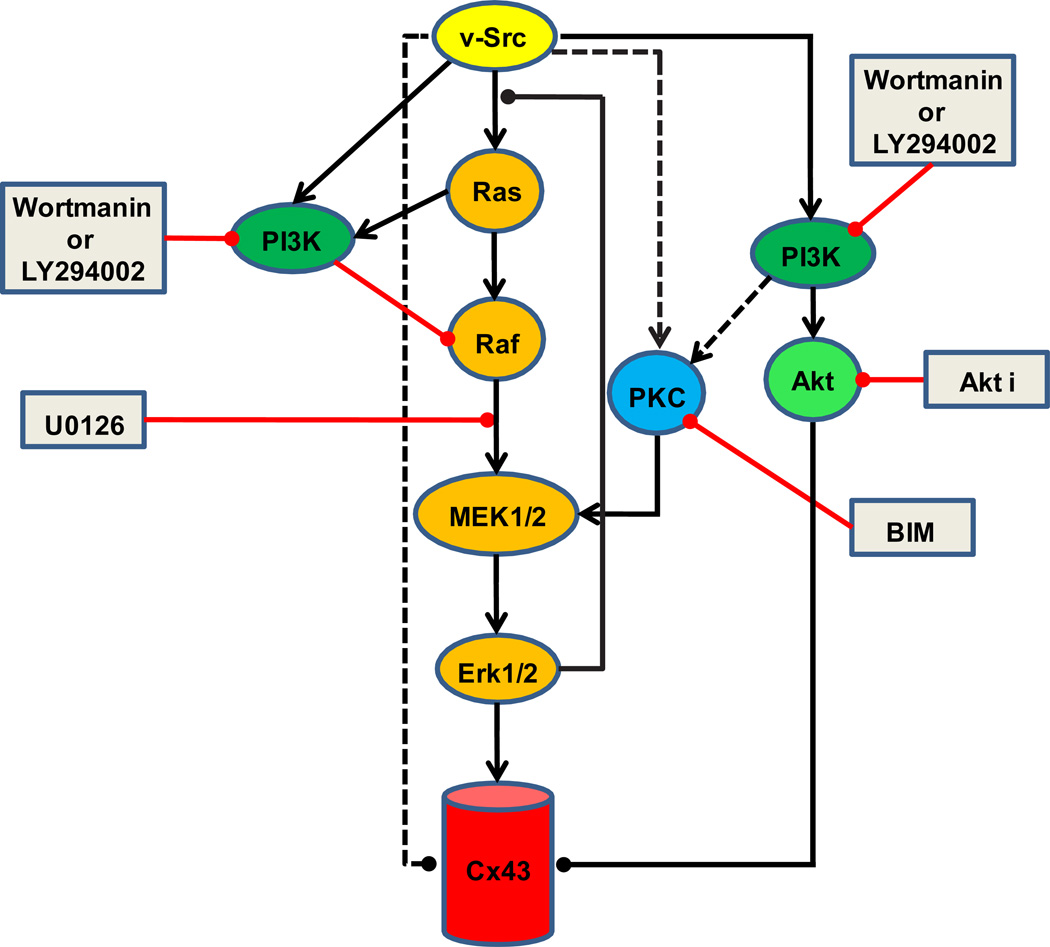
Fig. 8.
Model for signaling pathways involved in v-src induced initial closure of Cx43: The hypothetical model shown is based on the data presented here, and established (solid lines) or proposed connections (dashed lines) from other studies (see text). We have only noted the simplest model consistent with the data and literature, and more complex connections are possible. Activating effects are indicated by arrowheads (►), and inhibitory effects by lines with solid circles (●). The sites of action of the inhibitors (shown in grey rectangles) used in the current study are also indicated. The central player appears to be ERK1/2 (orange pathway). The PKC pathway (blue) can positively influence the activation of ERK1/2, but may also regulate Cx43 in a manner dependent on its very C-terminal ZO1 binding domain. PI3K (green) can contribute to src gating through PKC (and ERK?), or through Akt (light green), possibly by direct effects on Cx43 that have been reported. PI3K can also antagonize src gating of Cx43, in a yet to be defined pathway that inhibits ERK activation. Together, these pathways may serve to regulate the levels of ERK1/2 activation, perhaps keeping it within a defined range so as not to activate the negative feedback loop of ERK to the activator of Ras. However, since full activation of ERK by CA-MEK fails to induce channel closure, pathways independent of ERK, are likely to present parallel mechanisms for channel closure (dashed lines).