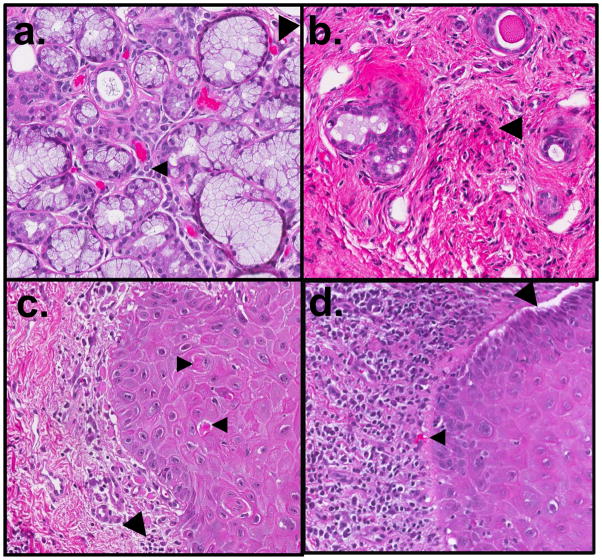
Figure 3.
Oral histopathologic changes in cGVHD include alterations in the minor salivary glands (MSG) and buccal mucosa. In the MSG, (a) sialadentis is often present, and fibrosis and atrophy of the gland are frequently observed. Lymphocytic infiltration (small arrow) and apoptotic cells (large arrow) may be observed in active stages of disease. (b) In late cGVHD, MSGs may have marked atrophy with only mild residual inflammation and few to no observable apoptotic cells. Destroyed glandular acini are often replaced by loose fibrotic stroma with associated lymphocytes (large arrow). In the buccal mucosal tissue, (c) generalized or band-like lymphocytic infiltration (large arrow) may be observed in the submucosa, near the junction of nonkeratinized squamous mucosa. Apoptotic cells (small arrows), often associated with lymphocytes, and may be observed in active stages of disease. (d) In severe cases, separation or clefting of the basal epithelial layer may be observed (large arrow), often in conjunction with heavy lymphocytic infiltrate and apoptotic bodies (small arrow). Original magnification 20×.