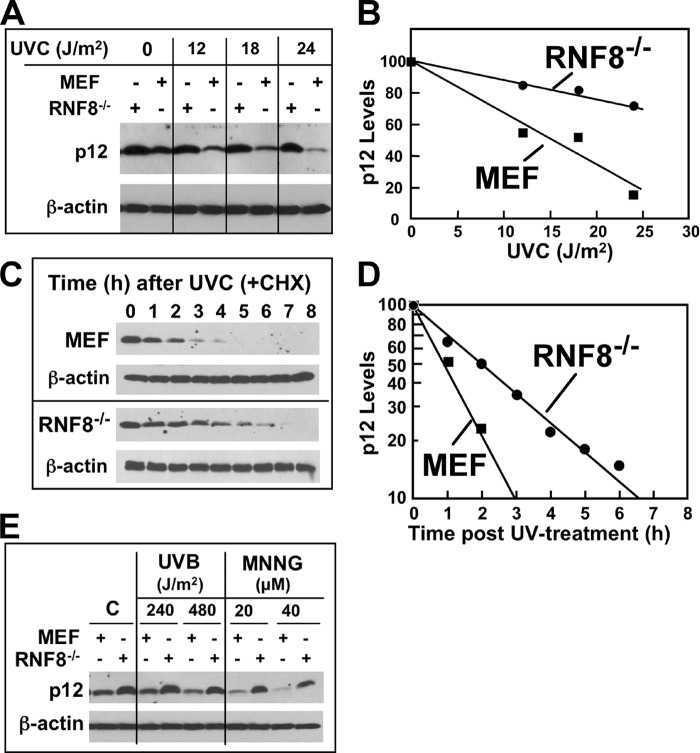
FIGURE 6.
UV-induced p12 degradation is impaired in mouse RNF8 knock-out cells. A, control MEF or their RNF8 knock-out cells (RNF8−/−) were treated with 0, 12, 18, and 24 J/m2 UVC, allowed to recover for 2 h, and analyzed by Western blotting for p12. β-Actin was used as a loading control. B, the relative amounts of p12 for the Western blots shown in panel A were determined by densitometry and corrected for loading against β-actin. Data were normalized to the p12 levels with no UV treatment and plotted against UV dose. C, time dependence of p12 degradation in RNF8−/− cells. Control MEF and RNF8−/− cells were treated with UVC (8 J/m2) and transferred to fresh medium containing 10 μg/ml cycloheximide (CHX). Cells were harvested at the indicated times (0–8 h) after treatment and analyzed by Western blotting for p12. D, the relative amounts of p12 for the Western blots shown in panel C were determined by densitometry as for panel B and were plotted on a semi-log plot against time. E, RNF8−/− and control MEF were treated with UVB (240 or 480 J/m2) and Western blotted for p12 after 4 h or treated with 20 or 40 μm MNNG and examined by Western blotting after 4 h.