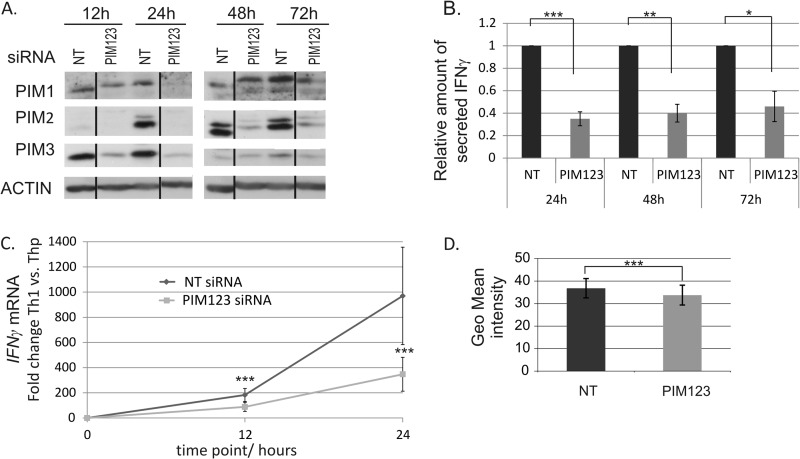
FIGURE 2.
Knockdown of PIM kinases down-regulates IFNγ at mRNA and protein levels during Th1 cell polarization. A, PIM1, PIM2, and PIM3 siRNAs efficiently inhibit the induction of PIM kinase expression in human CD4+ cells. Naïve CD4+ cells nucleofected with the indicated siRNAs were activated and polarized in the Th1 direction 20 h after nucleofection. Samples were harvested for Western blotting at the indicated time points. Representative data are shown from seven independent experiments. B, knockdown of PIM kinases inhibits IFNγ protein production. Cell culture supernatants from nucleofected and Th1-polarized cells were collected at the indicated time points, and the amount of IFNγ produced by the cells was measured by a cytokine assay. The bars represent the mean values ±S.E. (error bars) of the relative levels of IFNγ in PIM123 siRNA samples relative to the control samples. The values of the control samples were set as 1. Data collected from four to five independent experiments are shown. C, the induction of IFNγ mRNA is inhibited by PIM knockdown during early Th1 polarization. The levels of IFNγ mRNA in the nucleofected cells were analyzed by TaqMan RT-PCR. The graph represents the average -fold differences ±S.E. (error bars) of IFNγ mRNA levels in siRNA-treated Th1 cells compared with the average Thp value. D, PIM123 siRNA- or NT siRNA-nucleofected cells were cultured for 6 days under Th1-polarizing conditions. The cells where then harvested, and half of the cells were stimulated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and ionomycin, whereas the other half was left unstimulated. Cells were stained for intracellular IFNγ and analyzed with flow cytometry. Bars represent the average ±S.E. (error bars) geometrical (Geo) mean of fluorescence intensity calculated from four independent experiments. Vertical lines represent repositioned gel lanes that are from the same blot and the same exposure. Statistical significances were calculated using the two-tailed paired t test: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.02; ***, p > 0.01. siRNAs used were NT siRNA or PIM123 siRNAs.