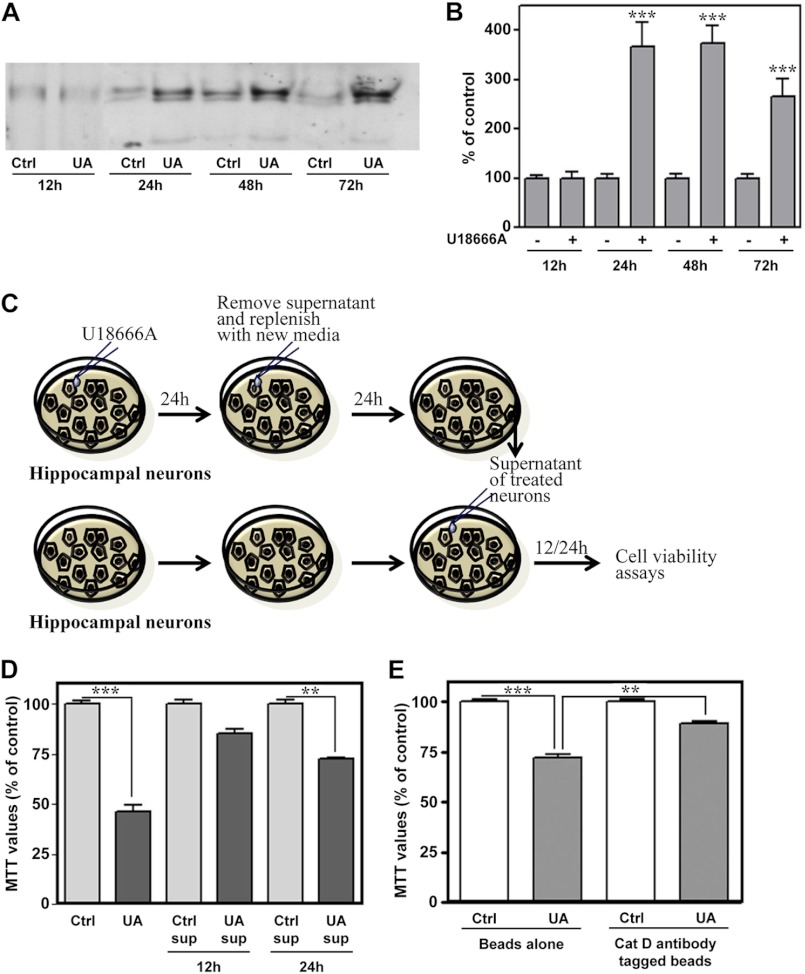
FIGURE 6.
U18666A treatment enhanced extracellular levels of cathepsin D in hippocampal neuronal cultures. A and B, immunoblots (A) and respective quantification (B) showing elevated cathepsin D levels in the conditioned medium of the neurons treated with 5 μg/ml U18666A for 12–72 h compared with respective control cultures. C, illustration of the experimental paradigm followed to study the influence of the conditioned medium containing extracellular cathepsin D on the viability of hippocampal neurons. D, toxicity induced by conditioned medium obtained from neurons treated for 24 h with or without 5 μg/ml U18666A. As evident from histograms, conditioned medium from UA18666A-treated neurons, but not from untreated neurons, can time-dependently reduce viability of hippocampal neurons as detected by the MTT assay. E, MTT assay revealed that toxicity induced by UA18666A-treated conditioned medium was partially reversed after depletion of cathepsin D in the media using cathepsin D antibody-coupled beads. All results, which are presented as means ± S.E. (error bars), were obtained from three separate experiments. Cat D, cathepsin D; Ctrl, control; sup, supernatant; UA, U18666A. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.