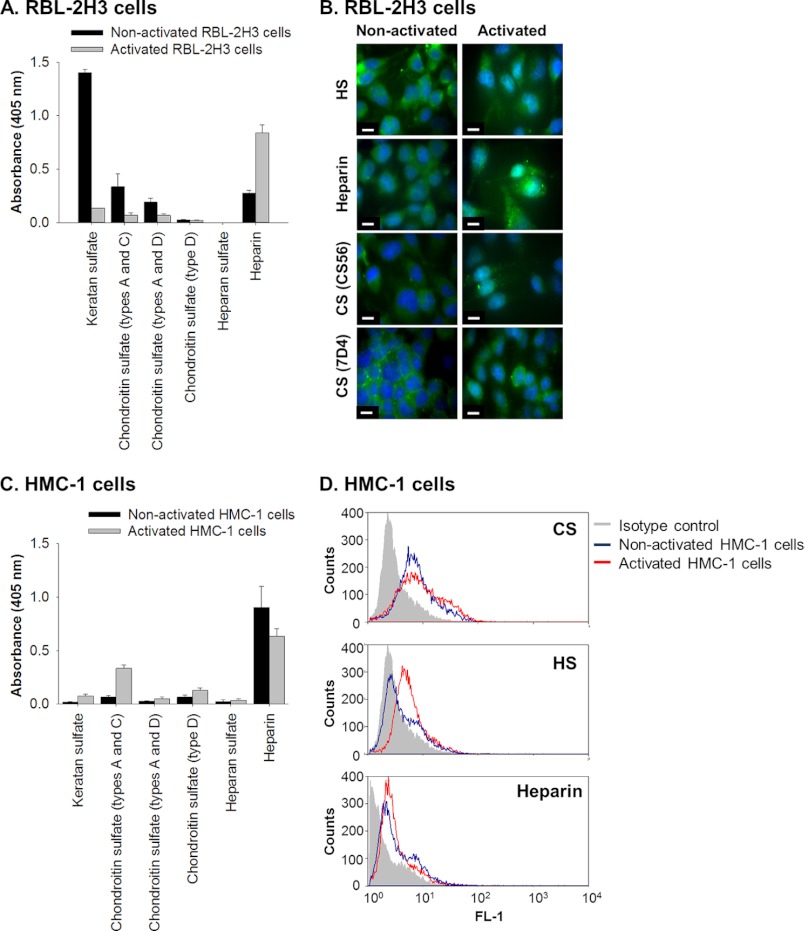
FIGURE 1.
Rat and human mast cell lines, RBL-2H3 and HMC-1, synthesize glycosaminoglycans. A, the presence of KS, CS, and HS and heparin in the proteoglycan-enriched fraction, isolated from medium conditioned by non-activated and activated (treated with PMA and A23187) RBL-2H3 cells, was identified by ELISA using monoclonal antibodies against KS (5-D-4), CS types A and C (CS-56), CS types A and D (LY-111), CS type D (MO-225), HS (F58-10E4), and heparin (2Q546). Wells were coated with 50 μl of a solution with a protein concentration of 100 μg/ml (absorbance readings were per 5 μg of coated protein). All absorbance readings were corrected for background and presented as mean ± S.D. (error bars) (n = 3). B, immunolocalization of glycosaminoglycans in cultures of RBL-2H3 isolated under non-activated and activated conditions. The presence of HS (HepSS1; A and B), heparin (2Q546; C and D), and CS (CS-56 and 7-D-4) was determined using antibodies against each of these glycosaminoglycans and visualized using FITC-conjugated secondary antibodies shown in green. Nuclei were stained with DAPI as shown in blue. Scale bars, 10 μm. C, the presence of KS, CS, and HS and heparin in the DEAE-enriched medium conditioned by non-activated and activated (treated with PMA) HMC-1 cells was identified by ELISA using the same set of monoclonal antibodies as described above: KS (5-D-4), CS types A and C (CS-56), CS types A and D (LY-111), CS type D (MO-225), HS (F58-10E4), and heparin (2Q546). All absorbance readings were corrected for background and presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). D, flow cytometry analyses were performed to detect the presence of HS (JM-403), CS (CS-56), and heparin (2Q546) by non-activated and activated HMC-1 cells. These experiments were controlled by comparing the readings obtained from the specific antibodies with those obtained using an irrelevant isotype antibody.