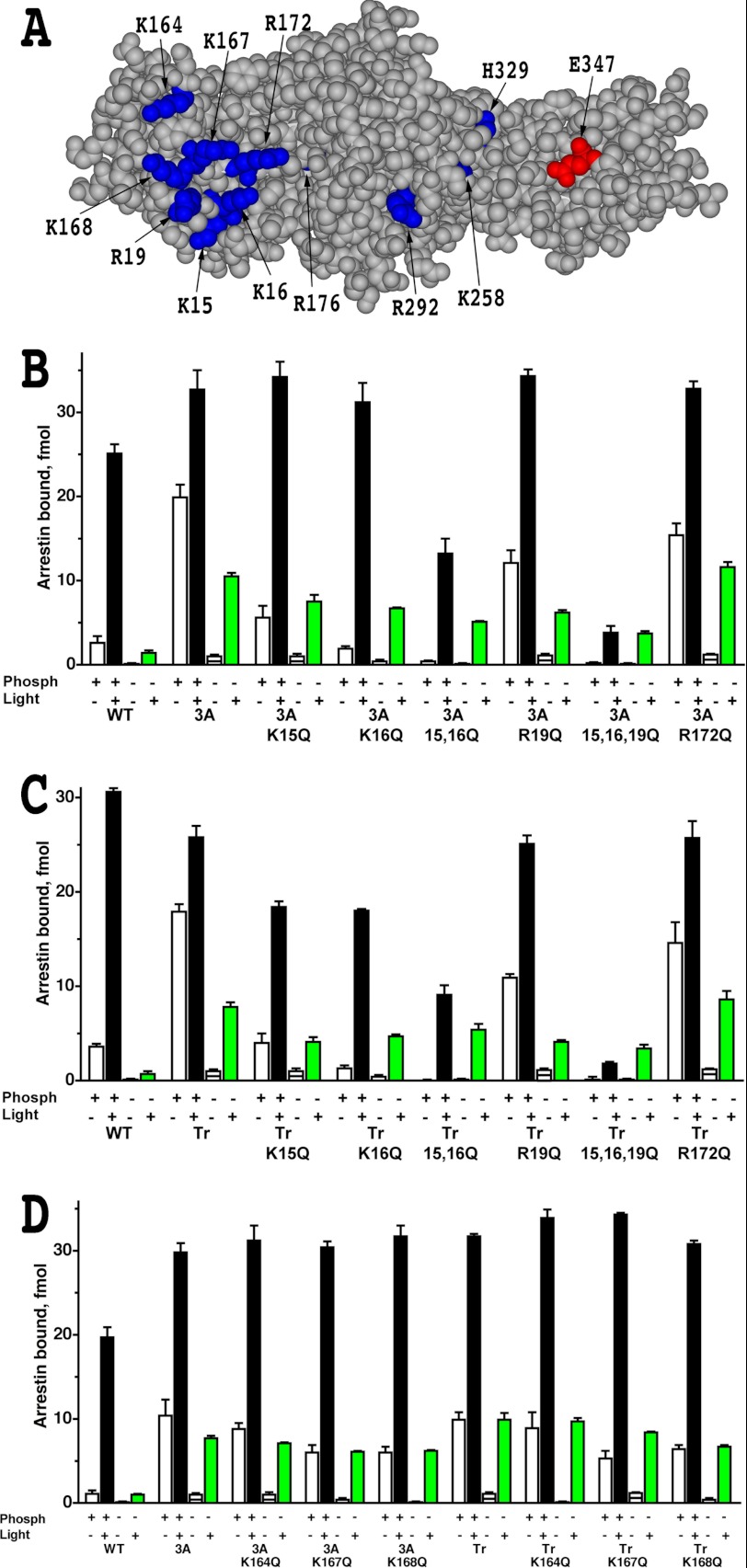
FIGURE 1.
Elimination of phosphate-binding residues does not improve the binding of phosphorylation-independent arrestin-1 mutants to Rh*. A, the structural model of mouse arrestin-1 (based on bovine arrestin-1 crystal structure PDB 1CF1 (37)) shows surface residues mutated in this study (blue, positive charges; red, negative charge). B–D, shown is the binding of WT mouse arrestin-1 and indicated N-domain (residues 1–177) mutants, where positively charged phosphate binding residues were replaced with glutamine, constructed on the background of either arrestin-1-(L374A/V375A/F376A) (3A) or truncated arrestin-1-(1–377) (Tr) to four functional forms of rhodopsin. The colors of the bars are: white, dark P-Rh; black, P-Rh*; horizontally striped, dark Rh; green, Rh*. The means ± S.D. of two experiments, each performed in duplicate, are shown. Note that R172Q is the only mutation that marginally increases Rh* binding of parental L374A/V375A/F376A and truncated arrestin-1-(1–377) mutants.