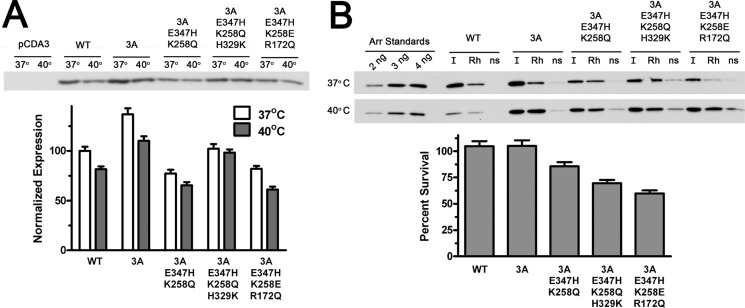
FIGURE 4.
Several mutants with the highest Rh* binding are stable in cellular environment. A, indicated forms of mouse arrestin-1 were expressed in HEK293 cells. For the last 3 h before lysis the cells were kept either at regular (37 °C) or elevated (40 °C) temperature. The levels of soluble arrestin-1 in lysates were determined by Western blot (upper panel) and expressed as percent of the level of WT arrestin-1 in cells kept at 37 °C (lower bar graph). B, functional activity of soluble arrestin-1 in lysates is shown. Equal volumes of lysates (10 μl) were incubated with (Rh) or without (ns) 1 μg of P-Rh*, and bound arrestin-1 was separated from free by centrifugation as described under “Experimental Procedures.” One-tenth of each pellet and input (I) was analyzed by Western blot (upper panel). Protein survival was calculated as the ratio of the fraction of arrestin-1 in lysate of cells incubated at 40 °C that specifically bound to P-Rh* to the bound fraction in lysates of control cells kept at 37 °C. Nonspecific binding (the amount of arrestin-1 pelleted in the absence of rhodopsin, likely due to aggregation) was subtracted from specific binding to P-Rh*. The means ± S.D. of two independent experiments, each quantified in two blots, are shown in both panels.