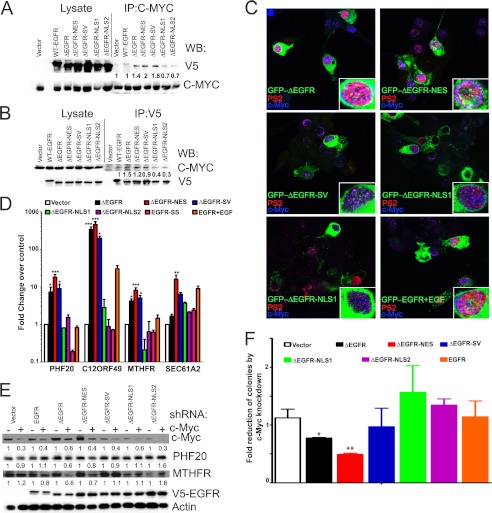
FIGURE 5.
Nuclear ΔEGFR associates with c-Myc to promote oncogenic phenotype in glioma cells. A, coimmunoprecipitation (IP) and Western blot (WB) analysis showing c-Myc association with ΔEGFR. Quantitation and statistical analysis of Western blotting are shown in supplemental Fig. S9A. B, coimmunoprecipitation and Western blot analysis showing ΔEGFR association with c-Myc. Quantitation and statistical analysis of Western blotting are shown in supplemental Fig. S9B. C, localization of GFP-EGFR, GFP-ΔEGFR, and GFP-tagged ΔEGFR mutants (green), phosphoPol2 (PS2, red), and c-Myc (blue) in U87 cells. The insets show magnification of a single cell for better visualization. D, sequential ChIP quantitative PCR analysis for c-Myc and the EGFR, ΔEGFR, and ΔEGFR mutants in stable U87 cells. The results have been normalized to the vector control. E, Western blot analysis of U87 stable cells after knockdown of c-Myc by shRNA. One representative blot of three replicates is shown. Quantitation and statistical analysis of Western blotting are shown in supplemental Fig. S9C. F, anchorage-independent colony formation analysis of U87 stable cells after knockdown of c-Myc by shRNA. Values are relative to vector control cells without c-Myc knockdown (normalized to 1). Error bars represent mean ± S.E. from three biological replicates. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.