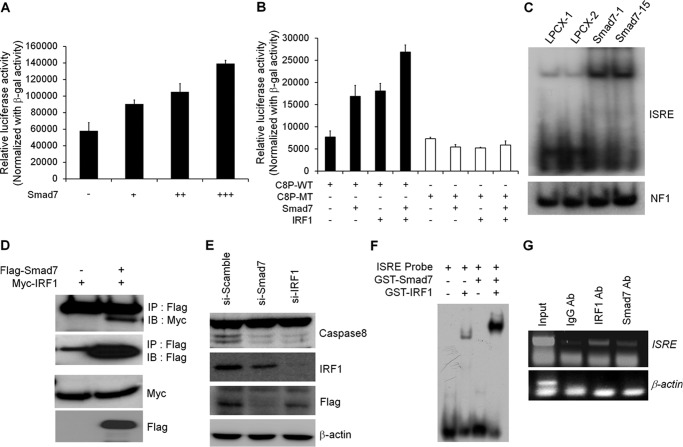
FIGURE 4.
Smad7 and IRF1 cooperate to induce caspase 8 expression. A, to test the involvement of IRF1-binding site, ISRE reporter assay was performed in MCF7 cells. After transfection with ISRE reporter construct with Smad7, cells were lysed to measure the luciferase activity. The values were normalized with β-galactosidase activity. B, wild-type or mutant ISRE reporter activity was measured after transfection with Smad7 alone or IRF1 together. The luciferase activity was normalized with β-galactosidase activity. C, after extraction of nuclear fractions from MCF7 cells, lysates were incubated with radiolabeled ISRE probe. Shifted bands were detected after running the gel and developing the autoradiography. The nuclear extracts were normalized with EMSA of the NF1 probe. D, to test the interaction of Smad7 with IRF1, expression vectors for Smad7 and IRF1 were transfected into HEK293 cells. Protein lysates were prepared and incubated with anti-FLAG antibody to precipitate Smad7 and interacting proteins. Immunoprecipitated (IP) IRF1 was detected with anti-Myc antibody. IB, immunoblot. E, to confirm the involvement of Smad7 and IRF1 in the expression of caspase 8, Smad7 or IRF1 was knocked down with siRNA. Each protein was detected with specific antibody to check the expression level of protein. F, to test the direct interaction of Smad7 on ISRE site, recombinant Smad7 or IRF1 proteins were isolated using glutathione-associated bead. Proteins were incubated with radiolabeled ISRE probe, and shifted bands were detected with autoradiography. G, to validate the interaction of Smad7 and IRF1 on caspase 8 promoter, ChIP assay was performed using antibodies against Smad7 or IRF1. Levels of protein recruitment to ISRE sites of the caspase 8 gene were measured by PCR and compared with input sample. As a negative control, β-actin primer was used.