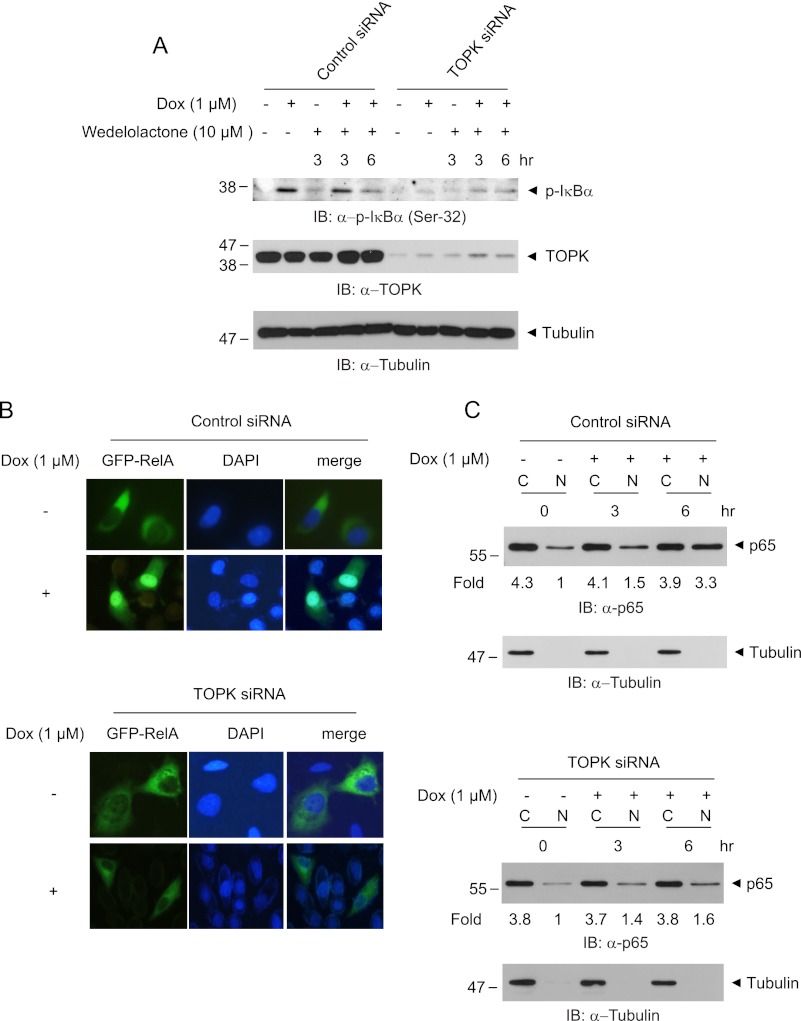
FIGURE 4.
Ablation of TOPK blocks IκBα phosphorylation and p65 nuclear translocation in response to doxorubicin. A, HeLa-TOPK siRNA cells or control siRNA cells were treated with doxorubicin (Dox, 1 μm) for the indicated times in the presence or absence of wedelolactone (10 μm). Phosphorylated IκBα, TOPK, or tubulin proteins were assessed with the respective antibodies. B, TOPK siRNA cells or control siRNA cells grown on cover glass were transfected with GFP-RelA. At 24 h post-transfection, the cells were stimulated with doxorubicin (1 μm) for 6 h. Cells mounted on slide glass were observed with fluorescent microscope. The nuclei were stained with DAPI, and representative photos of at least three independent experiments are shown. C, TOPK siRNA cells or control siRNA cells were incubated with doxorubicin (1 μm) for indicated time. The cells were harvested, and cytoplasmic extract (lanes C) or nuclear extract (lanes N) was prepared. The p65 level was evaluated using immunoblot (IB) analysis. ImageJ software was used for quantification.