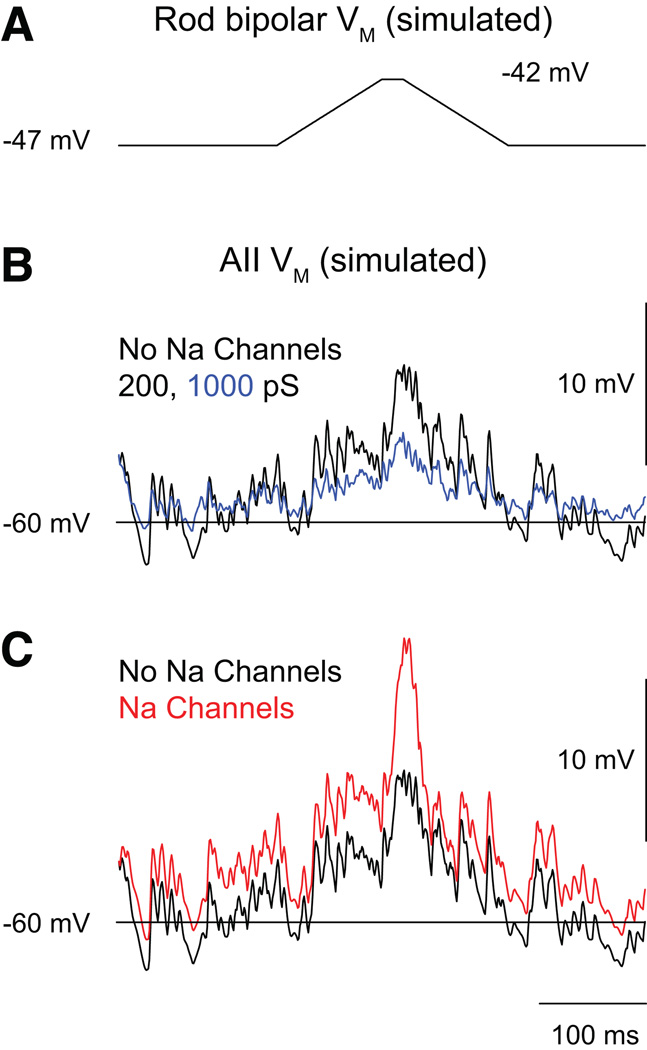
Figure 2. A computational model of the AII network predicts effects of coupling strength and Na channel expression on postsynaptic responses to divergent rod bipolar output.
(A) The voltage change in a single rod bipolar cell elicited by a “single-photon” response. The cell’s synaptic output diverges to five coupled AII amacrines. (B) the postsynaptic responses elicited when coupling strength (black = junctional conductance of 200 pS; blue = junctional conductance of 1000 pS) is altered. (C) the postsynaptic responses elicited when Na channel expression (black = no Na channels; red = Na channels present; junctional conductance = 200 pS) is varied. It is evident that the postsynaptic response is larger when the coupling conductance is low and Na channels are present. Figure modified from (Smith and Vardi, 1995).