Fig. 4.
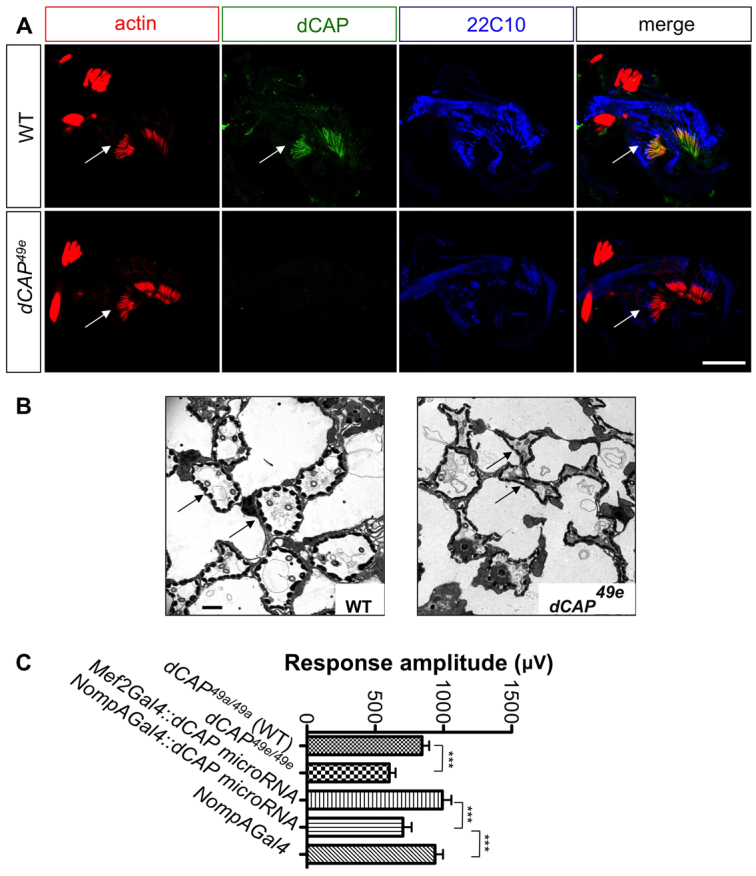
Audition defects in CAP mutants. (A) Antennal sections at the level of Johnston's organ from wild type and dCAP49e mutants immunostained with phalloidin (red), anti-CAP (green) and 22C10 antibody (blue). CAP colocalizes with phalloidin, which stains actin rods in scolopale cells (arrows). (B) Electron microscopic images of ultrathin sections from wild-type and dCAP49e Johnston's organs. CAP mutants show dysmorphic and collapsed scolopale cells (arrows). (C) Sound-evoked potentials recorded from the auditory nerves of adult flies. dCAP49e mutants (n=27 animals) and flies lacking CAP specifically in scolopale cells (n=21 animals) show a reduction in amplitude of response to sound when compared with controls (t-test: ***P<0.005). Data are mean±s.e.m. Scale bars: 30 μm in A; 1 μm in B.
