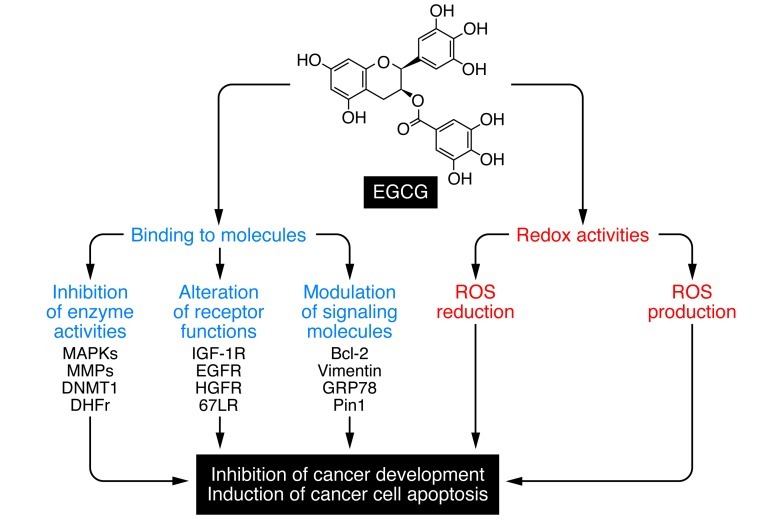
Figure 1. Proposed mechanisms of anticancer action of EGCG.
The mechanism by which EGCG exerts its antitumor actions is unknown, but may involve one or more of the actions illustrated. EGCG can act as an antioxidant, reducing ROS and inhibiting cancer development, and paradoxically may promote the production of ROS in cancer cells and induce apoptosis. EGCG is also known to bind and modulate the activities of enzymes, receptors, and signaling molecules that affect cell growth and proliferation. Activation of 67LR by EGCG and inhibition of PDE5 activity by its inhibitors synergistically induce cancer cell apoptosis (8). DNMT1, DNA, methyltransferase 1; DHFr, dihydrofolate reductase; HGFR, HGF receptor; Bcl-2, B cell CLL/lymphoma 2; GRP78, glucose-regulated protein 78 kDa; Pin1, peptidyl cis/trans isomerase.