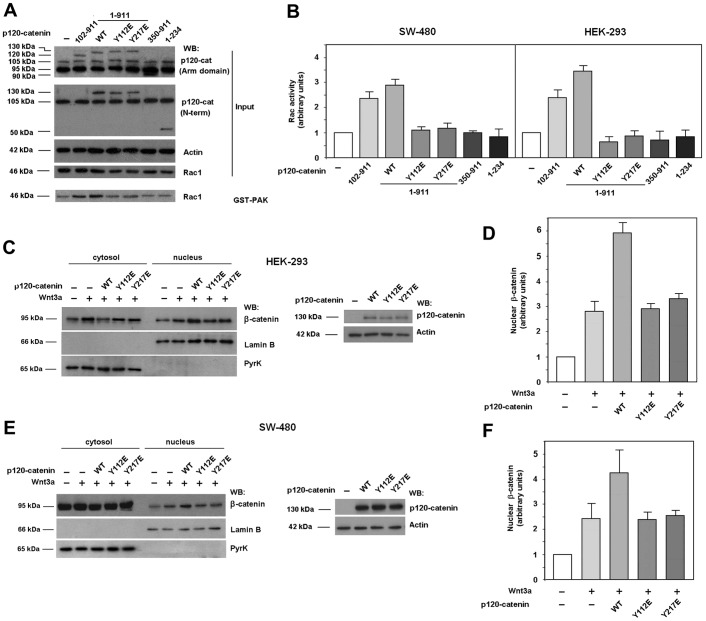
Fig. 4.
Only p120-catenin mutants able to interact with Rac1 and Vav2 induce Rac1 activation. (A) GST–PAK pull-down assays were performed in SW-480 cell extracts overexpressing either GFP–p120-catenin (p120-cat) wild-type (wt) isoforms 1 or 3, GFP–p120-catenin 1 harboring point mutants Y112E or Y217E, GFP–p120-catenin deletion mutants (350–911) or (1–234) or the empty vector phrGFP. Active Rac1 was detected by western blot (WB). (B) Autoradiograms from five different experiments performed in triplicate in SW-480 (left panel) and HEK-293 cells (right panel) were quantified and the mean ± s.d. was obtained for each condition. Each value is presented relative to that obtained in nonstimulated cells. (C–F) Cytosolic and nuclear lysates were obtained from HEK-293 (C,D) or SW-480 (E,F) cells overexpressing either GFP–p120-catenin wt isoform 1, GFP–p120-catenin point mutants Y112E or Y217E or the empty vector phrGFP, treated when indicated with Wnt3a-conditioned medium for 15 hours. The nuclear fraction was separated from the cytosolic and membrane-associated fraction as detailed in Materials and Methods. β-catenin levels in each cellular fraction were analyzed by WB. Lamin-β1 was used as a nuclear marker and pyruvate kinase as a marker for the cytosolic-plus-membrane fraction. In the right panel of C, p120-catenin wt, Y112E and Y217E expression levels were analyzed by WB. (D,F) Autoradiograms from four (F) or five (D) different experiments were quantified and the mean ± s.d. was obtained for each condition. Each value is presented relative to that obtained in nonstimulated and nontransfected cells.