Fig. 7.
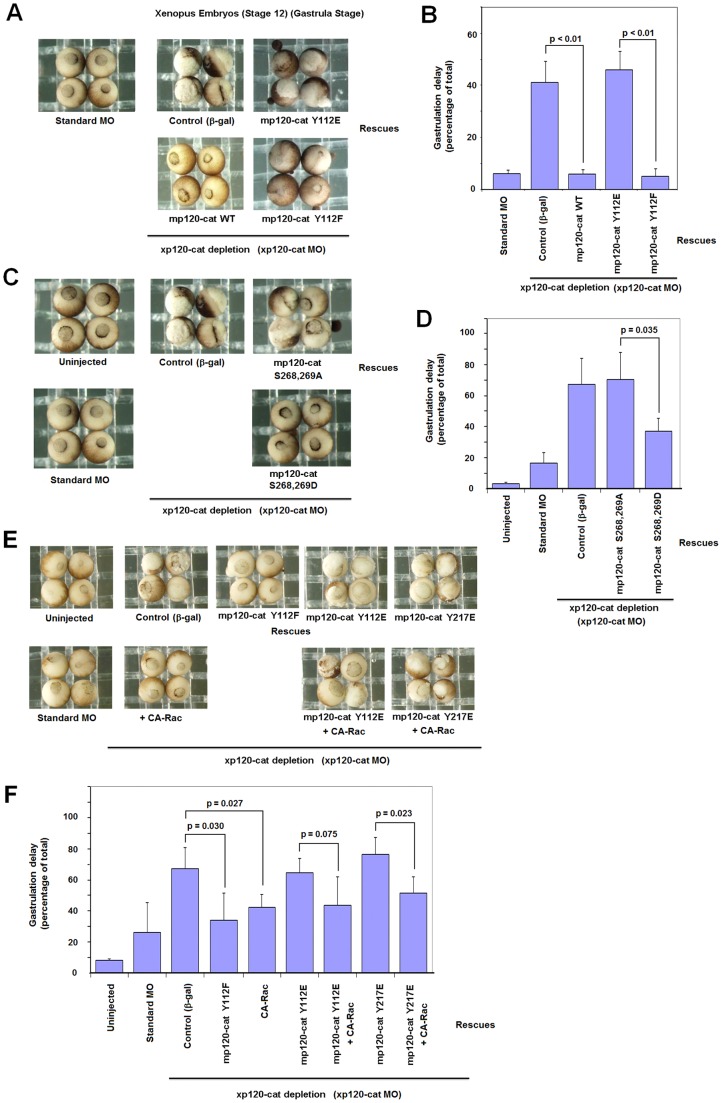
p120-catenin point mutants unable to bind Rac1 or Vav2 do not rescue gastrulation defects caused by p120-catenin depletion in Xenopus embryos. Embryos at the two-cell stage were injected with a control morpholino or a combination of xp120 morpholinos (20 ng each of xp120 MO I and MO II per blastomere). Rescues were performed by co-injection of xp120 morpholinos with in vitro transcribed mRNAs corresponding to mp120-catenin (mp120-cat) WT, mp120-catenin Y112E and mp120-catenin Y112F (A,B), or mp120-catenin Ser268,269A and mp120-catenin Ser268,269D (C,D). Embryos were scored at stage 12 (gastrula) for defects, including partial or improper closure of the blastopore. Representative resulting gastrulation phenotypes are shown in A and C, with percentages presented in B and D, including error bars. To avoid overexpression phenotypes, the injection doses of all rescuing constructs were carefully titrated to produce minimal effects when injected alone. (E) Embryos at the two-cell stage were injected with a control morpholino or a combination of xp120 morpholinos (20 ng each of xp120 MO I and MO II per blastomere). Rescues were performed by co-injection of xp120 morpholinos with mp120-catenin Y112F, CA-Rac, p120-catenin Y112E and mp120-catenin Y217E in vitro transcribed mRNAs. A small-rescue dose of CA-Rac1 was also co-injected with mp120 Y112E and mp120 Y217E constructs. Percentage of gastrulation delay from three different experiments is shown in (F). P values were determined using ANOVA.