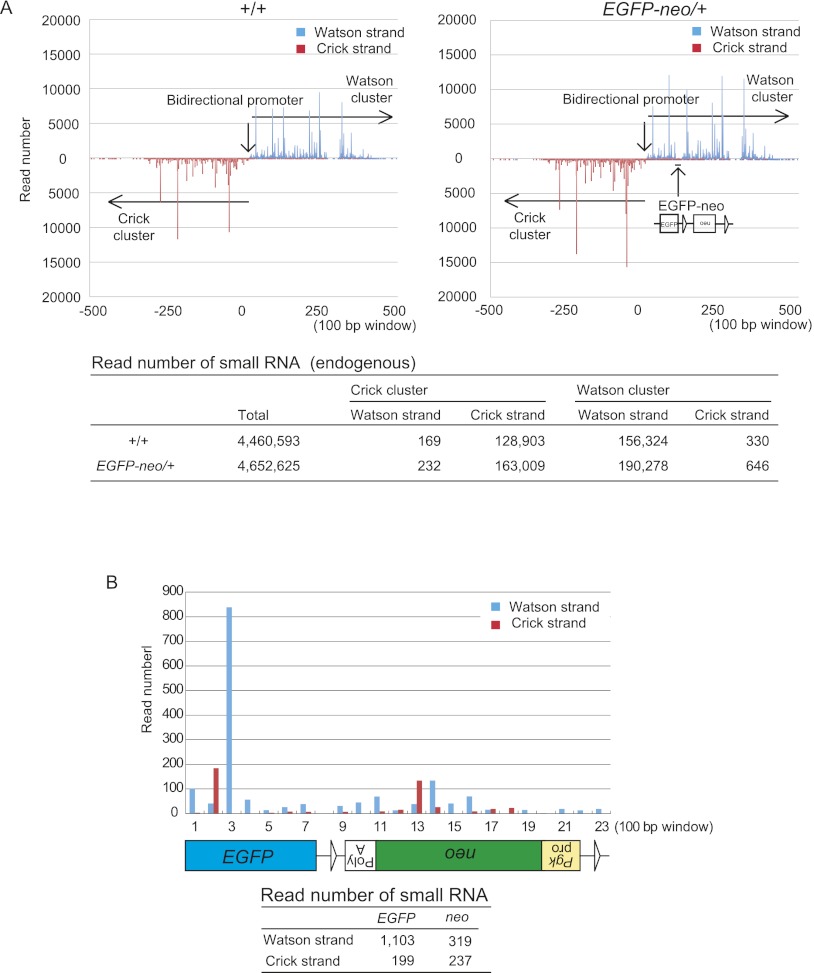
Figure 1.
Identification of small RNAs generated from the EGFP-neo knock-in sequence. A small RNA library prepared from 5-wk-old EGFP-neo/+ testes was subjected to high-throughput sequencing. (A) Distribution of endogenous small RNA sequences across the Watson and Crick clusters (mm9 chr.17: 27,409,752-27,511,260) in wild-type control (+/+) and EGFP-neo/+ testes. The data is shown for 100-bp windows across the region (top). The precise read numbers are also shown (bottom). The overall patterns in the wild-type and EGFP-neo+/– testes were very similar. (B) Distribution of small RNA sequences mapped within EGFP-neo. The small RNA read number for each 100-bp window is shown across the EGFP-neo fragment (top). The total read number for each strand of each gene is also shown (bottom).