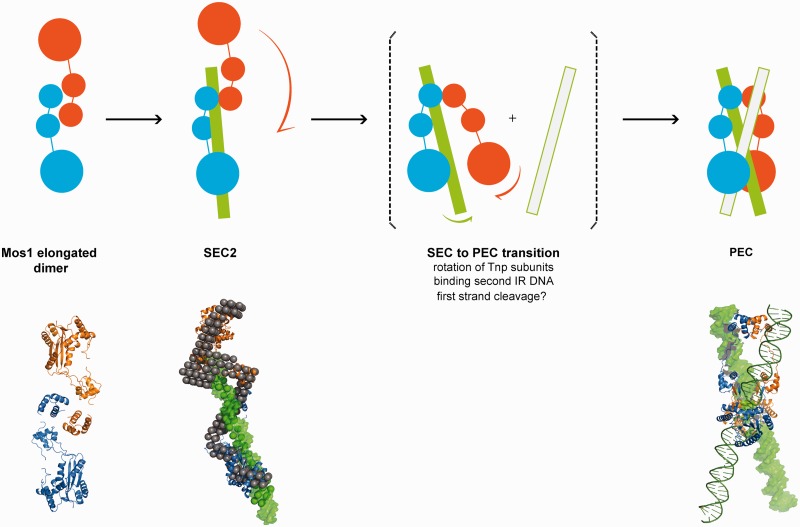
Figure 7.
Schematic mechanism of early steps in Mos1 transposition. Transposase (blue and orange monomers) exits as an elongated dimer in solution with the N-terminal domains at the central dimerization interface. When bound to one IR DNA in SEC2, the transposase dimer becomes more extended and the DNA (green) is predominantly associated with one monomer (blue); the other monomer (orange) may be more flexible. The phase model was interpreted by docking Mos1 monomers (ribbon) by eye to the protein phase and a 50 mer DNA duplex (green surface) to the DNA phase. The PEC could form by rotation of the flexible monomer about the HTH1 domain, accompanied by binding of the second transposon end. There may also be exchange of DNA between the two catalytic domains. Solution structures of the Mos1 dimer and SEC2, and the PEC crystal structure (3HOT) are shown below the schematic.