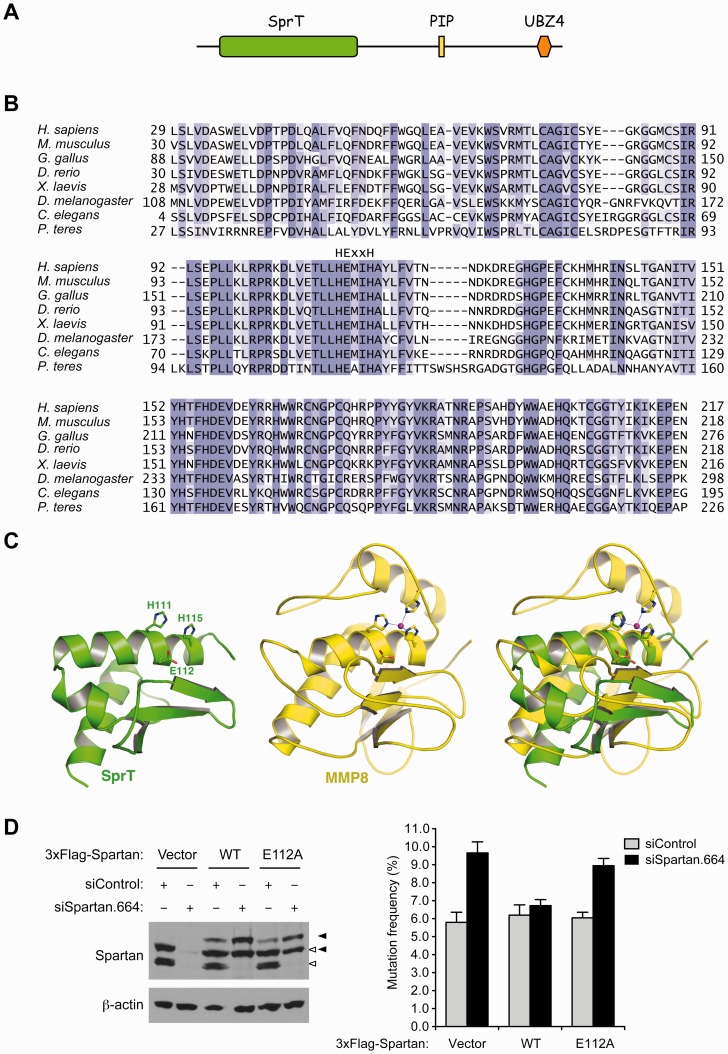
Figure 1.
The SprT domain of Spartan is a putative zinc metalloprotease and Glu112 is required for Spartan to suppress UV-induced mutagenesis. (A) Schematic representation of the domain structure of human Spartan. PIP, PCNA-interacting peptide; UBZ4, ubiquitin-binding zinc-finger 4. (B) Alignment of the SprT domain sequences from Spartan homologs in selected species. The HExxH motif is indicated above the sequences. (C) Model of a truncated human SprT domain (residues 43–121; generated by the Phyre server) showing the three residues of the HExxH motif (left); crystal structure of MMP8 (Protein Data Bank ID: 2OY4) showing the three residues of the HExxH motif and the zinc divalent cation coordinating three histidines (middle); overlay of the truncated SprT and MMP8 revealing the structural similarity in the active site between the two proteins (right). (D) Glu112 is required for suppression of UV-induced mutagenesis by Spartan. UV-induced mutagenesis was measured using the SupF shuttle vector system in 293 T cells transfected with the indicated siRNA oligos. Mutation frequencies are presented as percentage of mutant SupF genes. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). Wild-type or the E112A mutant of Spartan was expressed with 3xFlag tag in an siRNA-resistant form. Spartan proteins were analysed by Western blotting. Positions of endogenous and exogenous Spartan proteins are indicated by white and black arrowheads, respectively.